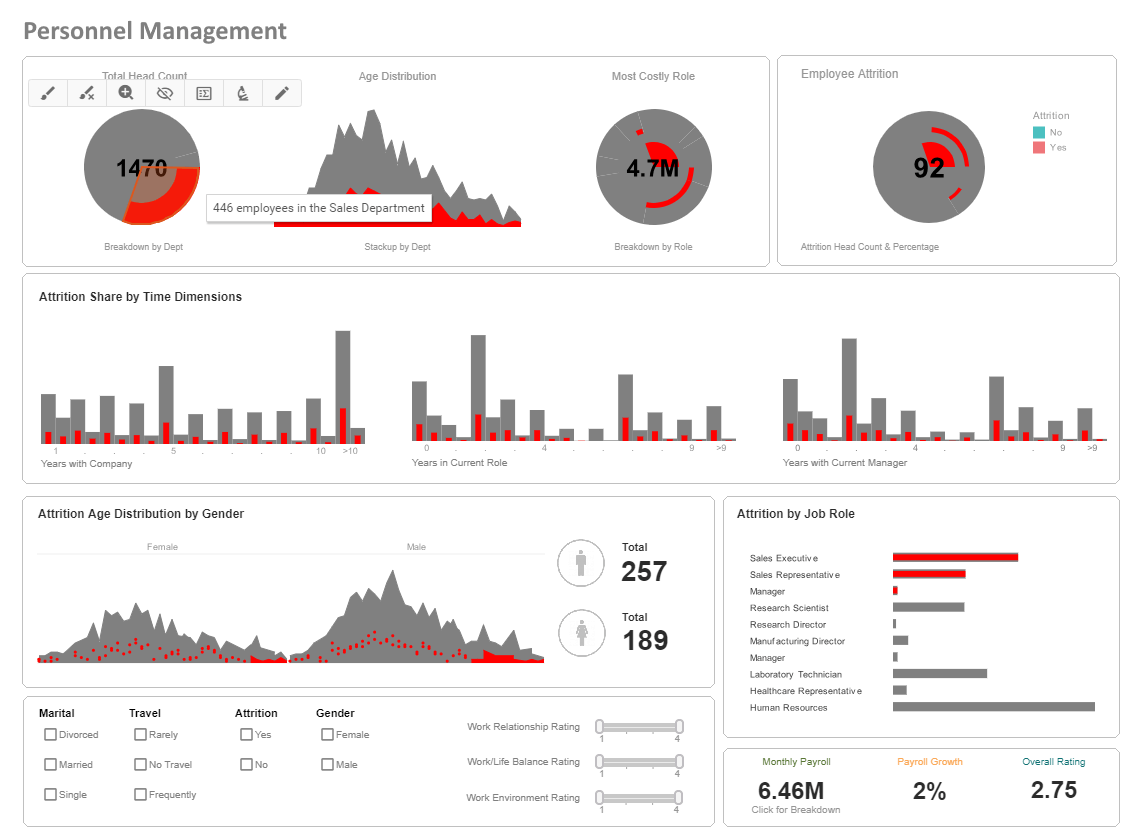
Better Payroll Dashboards for PeopleSoft
with
Maximum Self-Service
Powered by a Data Mashup Engine



Customer Service is the Best I've Encountered!
All the technicians are extremely knowledgeable, patient and will make every effort to accommodate your schedule and resolve the issue in a timely manner. - Jack from BOK Financial
Great Product and Easy to Use
I have been using this product for almost 2 years, and I find it simple to use and gives reliable results. I recently had a team trying to create a report for 2 weeks with another BI product. Since they couldn't build what they needed they came back to me. I was able to get it for them in less than a day with InetSoft. - Steven from Endurance Services
Explore Live Examples & Get Pricing Details
InetSoft does not sell or share your personal information to any third parties. Our privacy policy is available here.
Sample Customers






|






|
What Are the Drawbacks to PeopleSoft's Payroll Dashboards?
PeopleSoft's payroll dashboards offer valuable insights and functionalities for managing payroll processes within organizations. However, like any software solution, there are potential drawbacks that users may encounter when using PeopleSoft's payroll dashboards:
-
Complexity: One significant drawback of PeopleSoft's payroll dashboards is their complexity. PeopleSoft is known for its robust feature set and extensive customization options, but this can also make the software challenging to navigate and configure. Users may find it overwhelming to set up and customize the payroll dashboards to meet their specific needs, requiring extensive training and technical expertise.
-
Customization limitations: While PeopleSoft's payroll dashboards offer some degree of customization, there may be limitations in terms of flexibility and scalability. Users may find it difficult to tailor the dashboards to accommodate unique payroll processes or reporting requirements, leading to frustration and inefficiencies. Additionally, making changes to the dashboards may require specialized skills or involvement from IT personnel, which can further complicate the customization process.
-
Integration challenges: PeopleSoft's payroll dashboards may face integration challenges when interfacing with other systems or third-party applications. Integrating payroll data with other HR systems, financial software, or timekeeping solutions can be complex and time-consuming, especially if the systems use different data formats or protocols. This lack of seamless integration may result in data silos, inconsistencies, and manual data entry tasks, undermining the efficiency and accuracy of payroll processes.
-
Performance issues: Depending on the size and complexity of the organization, PeopleSoft's payroll dashboards may experience performance issues such as slow response times or system lag. Processing large volumes of payroll data and generating complex reports can strain the system's resources, leading to delays and interruptions in payroll processing. Users may experience frustration and productivity losses when waiting for the system to load or respond, particularly during peak periods such as payroll processing cycles.
What Features Are Required in a Good Payroll Dashboard?
A good payroll dashboard should encompass a range of features to effectively manage payroll processes, provide insights, and facilitate decision-making. Here are some key features that are often required in a good payroll dashboard:
-
Real-time Data Visualization: The dashboard should provide real-time visualization of payroll data, such as employee salaries, deductions, taxes, and benefits. Interactive charts, graphs, and tables allow users to quickly analyze trends, patterns, and outliers in payroll metrics, empowering decision-makers to make informed choices based on up-to-date information.
-
Customizable Reporting: A good payroll dashboard should offer customizable reporting capabilities to meet the diverse needs of users. Users should be able to generate and customize reports based on specific criteria, such as pay period, employee category, department, or location. Customizable report templates, filters, and drill-down options enable users to access the precise payroll data they need for analysis and compliance reporting.
-
Compliance Management: Compliance with local, state, and federal payroll regulations is crucial for avoiding penalties and legal risks. A good payroll dashboard should include features for managing compliance requirements, such as automatic tax calculations, wage and hour tracking, and audit trails. Alerts and notifications can also help users stay informed about changes in payroll laws and regulations.
-
Employee Self-Service: Providing employees with access to their payroll information and self-service capabilities can improve transparency, efficiency, and satisfaction. A good payroll dashboard should include employee self-service features, such as online pay stubs, tax forms, and direct deposit management. Self-service portals empower employees to view and update their payroll information securely, reducing administrative burdens on HR and payroll staff.
-
Integration with HR Systems: Seamless integration with human resources (HR) systems and other business applications is essential for streamlining payroll processes and ensuring data accuracy. A good payroll dashboard should integrate with HRIS (Human Resources Information Systems), time and attendance systems, benefits administration platforms, and accounting software. Data synchronization and automated workflows enable smooth data exchange between systems, eliminating manual data entry errors and redundancies.
-
Mobile Accessibility: In today's mobile-centric world, employees and managers expect access to payroll information anytime, anywhere. A good payroll dashboard should be mobile-responsive or offer dedicated mobile apps, allowing users to access payroll data and perform essential tasks from their smartphones or tablets. Mobile accessibility enhances user convenience, productivity, and engagement, particularly for remote or field-based employees.
-
Security and Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive payroll data from unauthorized access, breaches, or fraud is paramount. A good payroll dashboard should adhere to stringent security standards and data privacy regulations, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and audit logging. Regular security audits and updates help ensure the integrity and confidentiality of payroll data, instilling trust and confidence among users.