Maximum Self-Service for Business and Technical Users
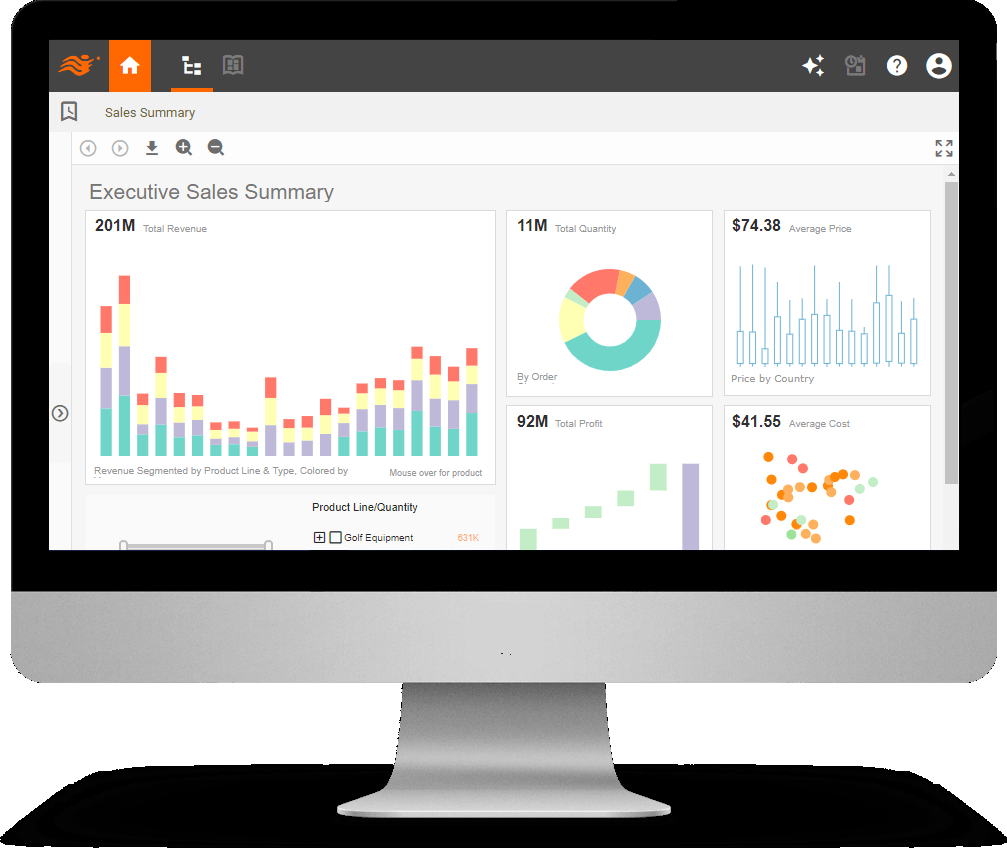
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytical Dashboards
Powered by a Data Transformation and Mashup Engine
Award winning, trusted by 5,000+ customers since 1996


Free start:
Open source StyleBI is free to use
Free account for StyleBI Online Application
Business Users: Interactive Dashboards with Rich Customization and Self-Service

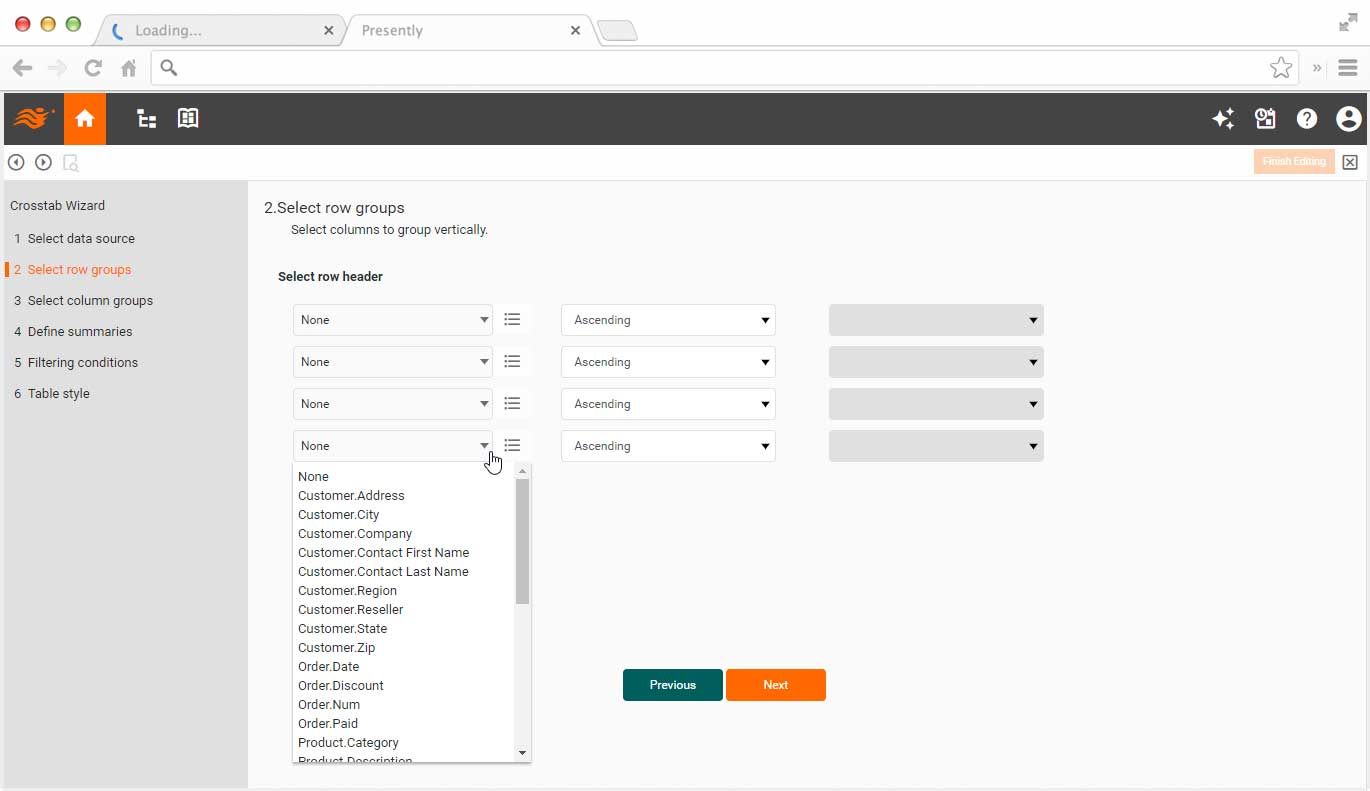
Designers: Rapidly Prepare Data and Design Dashboard Reports

Sample Customers












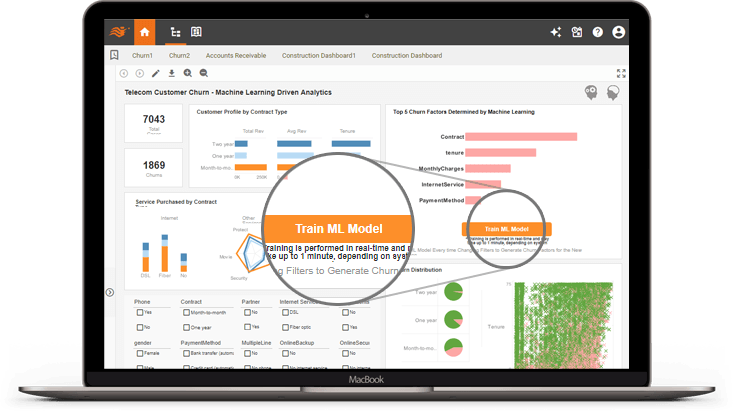
Data Specialists: Mashup Machine Learning with Business Intelligence
How Do Operators of Nursing and Residential Care Facilities Use Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence encompasses the processes, technologies, and strategies used to analyze and interpret data to support decision-making. In the context of nursing and residential care facilities, BI tools are employed to gain insights into various aspects of operations, including resident care, staffing, financial management, and regulatory compliance.
-
Resident Care Optimization: BI enables operators to monitor and analyze data related to resident health outcomes, satisfaction levels, and service utilization patterns. By tracking metrics such as medication adherence rates, incidence of falls, and hospital readmission rates, operators can identify areas for improvement and implement targeted interventions to enhance the quality of care delivered to residents.
-
Staffing Management: Effective staffing is essential for ensuring resident safety, satisfaction, and quality of care. BI tools allow operators to analyze staffing levels, staff-to-resident ratios, and employee turnover rates to optimize workforce allocation and scheduling. By identifying staffing shortages or overages in real-time, operators can adjust staffing levels accordingly to maintain optimal care standards while controlling labor costs.
-
Financial Performance Monitoring: Nursing and residential care facilities operate within tight budget constraints, making financial management a top priority. BI solutions facilitate the analysis of revenue streams, expenditure patterns, and billing processes to improve financial performance and profitability. Operators track metrics such as revenue per resident day, average length of stay, and accounts receivable aging to identify revenue opportunities, reduce costs, and enhance cash flow.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements is critical for nursing and residential care facilities to maintain licensure and accreditation. BI tools enable operators to track compliance metrics, such as staff training certifications, documentation completeness, and survey outcomes, to ensure adherence to regulatory standards. By proactively identifying areas of non-compliance, operators can implement corrective actions and mitigate risks of penalties or sanctions.
Key Metrics and KPIs Tracked by Operators:
Operators of nursing and residential care facilities track a variety of metrics and KPIs to assess performance, drive improvement initiatives, and achieve organizational objectives. Some of the key metrics and KPIs commonly monitored include:
-
Occupancy Rate: The percentage of available beds or units that are occupied by residents. A high occupancy rate indicates strong demand for services and optimal utilization of facility resources.
-
Average Length of Stay: The average duration of time that residents stay in the facility before discharge or transfer. Monitoring this metric helps operators understand resident turnover rates and plan for capacity management.
-
Staff Turnover Rate: The percentage of employees who leave their positions within a specified period. High staff turnover can negatively impact continuity of care, morale, and operational efficiency.
-
Medication Error Rate: The frequency of errors or discrepancies in medication administration documented through incident reports or quality audits. Minimizing medication errors is crucial for resident safety and regulatory compliance.
-
Patient Satisfaction Scores: Feedback from residents and their families regarding their experiences with care services, amenities, and overall satisfaction. Improving patient satisfaction scores enhances resident retention and reputation management.
-
Revenue per Resident Day: The average revenue generated per resident per day of stay, calculated by dividing total revenue by total resident days. Increasing revenue per resident day contributes to financial sustainability and profitability.
-
Staffing Ratio: The ratio of staff members to residents, typically measured for different shifts and care units. Maintaining appropriate staffing ratios ensures adequate supervision, assistance, and support for residents' needs.