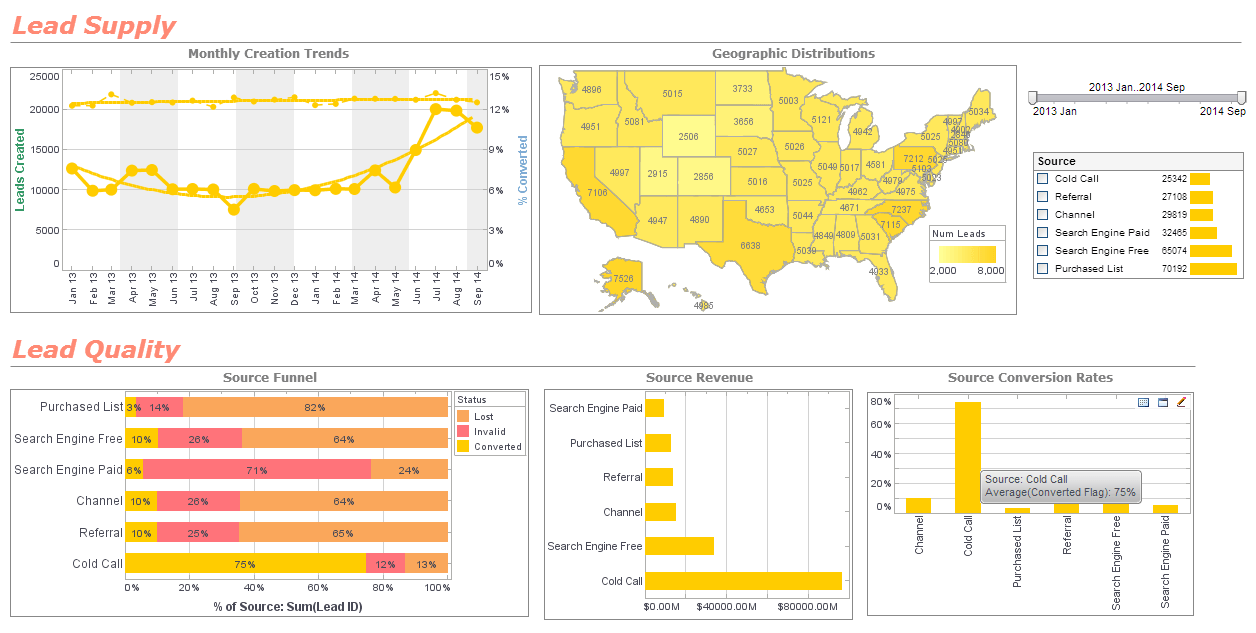
Business Intelligence Data
Every day, businesses produce near-endless amounts of data. Something as simple as an employee's lunch schedule can lead to great insight into sales patterns if approached from the right angle. This is where business intelligence becomes a key tool for managers. Through data analysis, business intelligence operations enable raw data to become actionable data for decision making.
Creating Reports
InetSoft helps you make sense of your data with StyleBI, the premier business intelligence suite. StyleBI provides your organization with top-of-the-line enterprise reporting capabilities through a 100% Web-based, zero-client, application. You users can create ad hoc reports, production reports, or any other kind of reports through an intuitive drag-and-drop designer. Users require no formal training, as they can just drag data in the form of visual blocks together to create joins, unions, etc. Data can be placed into tables, charted, or freely positioned to suit the individual needs of each user. Textual data can be placed in any report with a common word processor-style interface.
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
Viewing Reports
Created reports can be quickly and effortlessly shared in several ways. First and foremost, reports can be exported to various file formats, including Excel, PowerPoint, and PDF, to be quickly disseminated across your organization. Reports can be shared via Web-enabled mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets as well as desktop machines via Web Browser.
Report viewing can be customized, allowing the report creator to filter, sort, or even hide data from various parties. These reports can also be drilled into to view underlying data, sources, or other embedded documents.
What Data Is Collected in Zoonotic Disease Research?
Zoonotic disease research involves the collection of various types of data to understand the transmission, epidemiology, and impact of diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans. Here are some key types of data collected in zoonotic disease research:
-
Pathogen Data: This includes information about the infectious agents responsible for zoonotic diseases, such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi. Researchers collect data on the genetic makeup, virulence factors, antigenicity, and drug resistance patterns of these pathogens to understand their behavior and potential for transmission.
-
Host Data: Data about the animal hosts of zoonotic diseases is essential for understanding disease dynamics and transmission pathways. This includes data on the species, populations, demographics, behavior, physiology, and immune responses of animals that serve as reservoirs or intermediate hosts for zoonotic pathogens.
-
Human Data: Understanding the human side of zoonotic diseases involves collecting data on human populations at risk, including demographics, behaviors, occupations, travel patterns, and health status. Epidemiological data on human cases, including symptoms, outcomes, and exposure histories, are crucial for identifying risk factors and transmission routes.
-
Vector Data: Many zoonotic diseases are transmitted to humans through vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, or other arthropods. Collecting data on vector species, abundance, distribution, habitat preferences, and feeding behaviors helps researchers understand their role in disease transmission and develop targeted control strategies.
-
Environmental Data: Environmental factors play a significant role in zoonotic disease transmission and ecology. Researchers collect data on environmental variables such as climate, temperature, humidity, precipitation, land use, vegetation cover, water quality, and habitat fragmentation to assess their impact on pathogen survival, vector abundance, and host distribution.
-
Genomic Data: Advances in genomics have revolutionized zoonotic disease research by enabling the sequencing and analysis of pathogen genomes, host genomes, and microbiomes. Genomic data provide insights into the evolution, transmission dynamics, host specificity, and adaptation of zoonotic pathogens, as well as host genetic susceptibility to infection.
-
Surveillance Data: Surveillance systems are used to monitor zoonotic diseases in both animal and human populations. This includes passive surveillance (reporting of cases by healthcare providers or veterinarians) and active surveillance (systematic data collection through surveys, screenings, or diagnostic testing). Surveillance data help identify emerging threats, monitor disease trends, and guide control measures.
-
Ecological Data: Zoonotic disease transmission occurs within complex ecological systems involving interactions between pathogens, hosts, vectors, and the environment. Ecological data, including biodiversity, ecosystem health, species interactions, and ecological disturbances, provide context for understanding disease ecology and predicting disease emergence.
-
Social and Behavioral Data: Zoonotic disease research also involves collecting data on human behaviors, cultural practices, socioeconomic factors, healthcare access, and risk perceptions related to disease transmission and prevention. Understanding human-animal interactions and socio-cultural contexts is crucial for designing effective interventions and communication strategies.
How Is Artificial Intelligence Used in Zoonotic Disease Treatment?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being utilized in various aspects of zoonotic disease treatment, including diagnosis, drug discovery, treatment optimization, and outbreak prediction. Here are some ways AI is being used in zoonotic disease treatment:
-
Diagnostic Assistance: AI algorithms can analyze medical imaging data, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, to assist in the diagnosis of zoonotic diseases. For example, AI-based image recognition systems can help identify characteristic patterns or lesions associated with zoonotic infections, enabling early detection and prompt treatment.
-
Pathogen Identification: AI algorithms can analyze genomic data from pathogens to identify genetic markers, virulence factors, and drug resistance mutations. This information can aid in the rapid and accurate identification of zoonotic pathogens, guiding treatment decisions and surveillance efforts.
-
Drug Discovery and Development: AI-powered computational methods, such as machine learning and molecular modeling, are being used to accelerate the discovery of novel drugs and therapeutic targets for zoonotic diseases. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets of chemical compounds, biological assays, and genomic information to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety profiles.
-
Personalized Treatment Planning: AI-based decision support systems can analyze patient data, including clinical history, genetic profiles, and treatment responses, to tailor treatment plans to individual patients. This personalized approach can optimize treatment efficacy, minimize adverse effects, and reduce the development of drug resistance in zoonotic disease treatment.
-
Drug Repurposing: AI algorithms can analyze existing drugs and their molecular targets to identify potential candidates for repurposing in the treatment of zoonotic diseases. By repurposing drugs that have already been approved for other indications, AI can expedite the development of new treatments and reduce costs.
-
Predictive Modeling for Outbreak Management: AI-based predictive modeling techniques can analyze epidemiological data, environmental factors, and human behavior patterns to forecast the spread of zoonotic diseases and inform outbreak response strategies. These models can help public health authorities allocate resources, implement control measures, and mitigate the impact of outbreaks.
-
Real-time Surveillance and Monitoring: AI algorithms can analyze data from diverse sources, including social media, news reports, healthcare records, and environmental sensors, to detect early warning signs of zoonotic disease outbreaks. By monitoring for signals of emerging threats, AI can facilitate rapid response and containment efforts.
-
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: AI-powered telemedicine platforms and wearable devices can enable remote consultation and monitoring of patients with zoonotic diseases, particularly in remote or underserved areas. These technologies can improve access to healthcare services, facilitate early intervention, and reduce transmission risks.
 |
View live interactive examples in InetSoft's dashboard and visualization gallery. |
More Articles About BI Data Applications
AI-Powered NLP for Call Classification - If you have a big company, working with millions of customers on a daily basis, you might also have a customer service that consists of different departments. Here's where you can face the issue of the right person getting the right ticket to solve. This problem can be resolved through the AI-powered feature called neuro-linguistic processing. This feature works with the inquiries to help customer service sort out, classify and rout written messages as well as calls. This is a helpful feature that gets a customer's message to the right department to resolve it quicker...
Developing Dynamic Supply Chain Models - Supply chain models are relatively volatile because of customer demands and supplier relationships. All of this can become overwhelming for those overseeing supply chain models. Regardless of what level a company is in on a supply chain model, using a dashboard that provides real-time business intelligence is crucial for efficient operations. A supply chain monitoring analytical system providing real-time insights can help schedule tasks appropriately...
Manipulate Apache Spark Data - Nowadays all companies struggle with ever growing stores of data. Due to the increase in data storage technology, data sources have become larger and old fashioned data tools won't cut it. Big Data is hard to manage, move, report, and analyze. This is where InetSoft comes in. With some traditional tools the user may be able to look at the data, but not in real-time. Basic data tools won't deliver with the same speed and efficiency that InetSoft's Apache Spark dashboard software will. Information can also be extracted that normal data tools are unable to replicate. This creates knowledge that otherwise wouldn't exist without InetSoft...
Resources for Business Intelligence Beginners - Looking for an introduction to business intelligence? InetSoft is a BI software provider, and here you can view demos, see customer examples, and read articles explaining the basics of BI and best practices for implementing successful business intelligence...