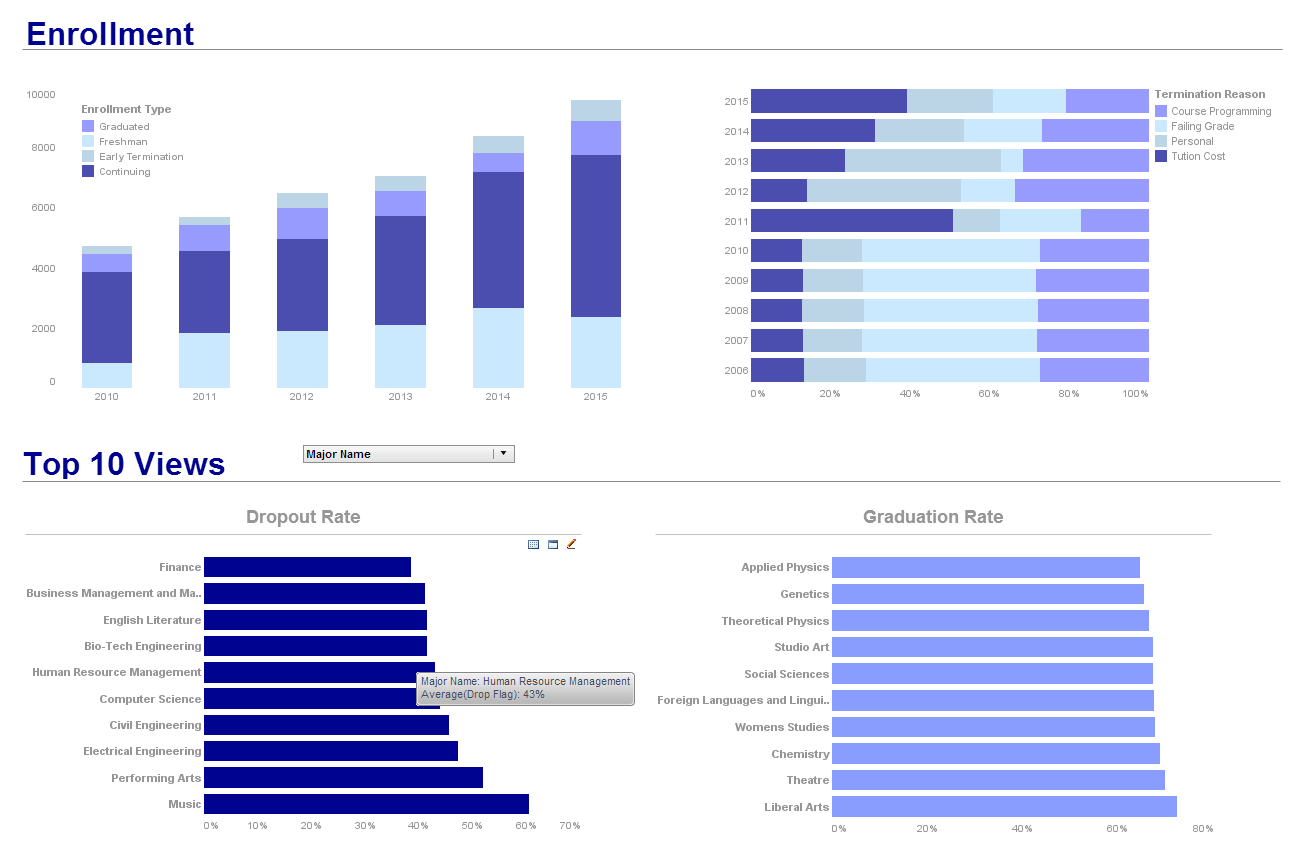
Try InetSoft's Dashboard Reporting Software
Are you looking to download dashboard reporting software? Since 1996 InetSoft has been making dashboard software that is easy to deploy and easy to use. Build self-service oriented dashboards quickly. View a demo, try it online for free, and request a free download.
Why InetSoft?
InetSoft's dashboard reporting software is easy enough to be:
- Deployed in just weeks
- Learned by end users with minimal training
- Used by any executive without the aid of IT
agile enough to be:
- Adaptable to changing data and business needs
- Used for data exploration through visualization
- Capable of maximum self-service
and robust enough to:
- Attract the attention of executives
- Meet the demands of power users
- Scale up for organizations of any size
Evaluate Style Scope from InetSoft. It's Easy. Agile. & Robust.
Register for more info and to download free eval software
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions. Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting. InetSoft's patent pending Data Block™ technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup.
This capability combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft's visual analysis technologies allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer. InetSoft was rated #1 in Butler Analytics Business Analytics Yearbook, and InetSoft's BI solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries.

What KPIs and Statistics Are Used in Arbitrage Trading?
Arbitrage trading involves taking advantage of price discrepancies between different markets or instruments. To effectively engage in arbitrage, traders use various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and statistics to measure performance and manage risk. Here are some of the key KPIs and statistics used in arbitrage trading, along with their definitions and significance:
1. Profitability Metrics
- Gross Profit: The total revenue generated from arbitrage trades before deducting expenses. It is significant as it shows the potential of the trading strategy to generate income.
- Net Profit: Gross profit minus trading costs, taxes, and other expenses. This is crucial as it represents the actual earnings from the trading activities.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculated as (Net Profit / Initial Investment) * 100%. ROI measures the efficiency of the investment, helping traders understand the profitability relative to the amount invested.
2. Risk Metrics
- Value at Risk (VaR): An estimate of the potential loss in value of a portfolio over a defined period for a given confidence interval. It helps in understanding the risk exposure and potential maximum loss.
- Sharpe Ratio: Calculated as (Average Return - Risk-Free Rate) / Standard Deviation of Return. It measures risk-adjusted return, indicating how much return is generated per unit of risk.
- Maximum Drawdown: The maximum observed loss from a peak to a trough before a new peak is achieved. It helps in assessing the risk of significant losses in the trading strategy.
3. Performance Metrics
- Alpha: The excess return of an investment relative to the return of a benchmark index. In arbitrage trading, alpha indicates the additional value created by the strategy.
- Beta: A measure of the volatility of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole. Beta helps in understanding the sensitivity of the arbitrage strategy to market movements.
- Win Rate: The percentage of profitable trades out of the total number of trades. A higher win rate indicates a higher probability of success in arbitrage opportunities.
4. Efficiency Metrics
- Execution Time: The time taken to execute a trade from the moment an arbitrage opportunity is identified. Faster execution times can capture more opportunities and reduce the risk of price movements.
- Transaction Costs: All costs associated with executing trades, including brokerage fees, spreads, and slippage. Minimizing transaction costs is essential for maximizing net profits.
- Turnover Rate: The frequency at which the assets in the portfolio are traded. High turnover rates might indicate active trading but can also lead to higher transaction costs.
5. Liquidity Metrics
- Market Depth: The volume of buy and sell orders in the order book at various price levels. High market depth indicates better liquidity, making it easier to execute large trades without significant price impact.
- Bid-Ask Spread: The difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. Narrow spreads indicate high liquidity and lower trading costs.
6. Operational Metrics
- Error Rate: The frequency of errors in trade execution, including mismatches, failures, and other operational issues. Low error rates are critical for maintaining the efficiency and profitability of arbitrage trading.
- System Uptime: The percentage of time the trading system is operational and available for executing trades. High system uptime ensures continuous monitoring and exploitation of arbitrage opportunities.
Significance of KPIs and Statistics in Arbitrage Trading
- Performance Monitoring: KPIs help traders continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of their arbitrage strategies, ensuring they meet desired performance standards.
- Risk Management: By tracking risk metrics, traders can identify potential threats and adjust their strategies to mitigate losses and protect their investments.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficiency metrics provide insights into the operational aspects of trading, highlighting areas where processes can be improved to enhance overall performance.
- Decision Making: Accurate and timely data from these KPIs enable traders to make informed decisions, improving the likelihood of capturing profitable arbitrage opportunities.
- Benchmarking: Comparing these metrics against industry benchmarks or historical performance helps traders understand their competitive position and identify areas for improvement.
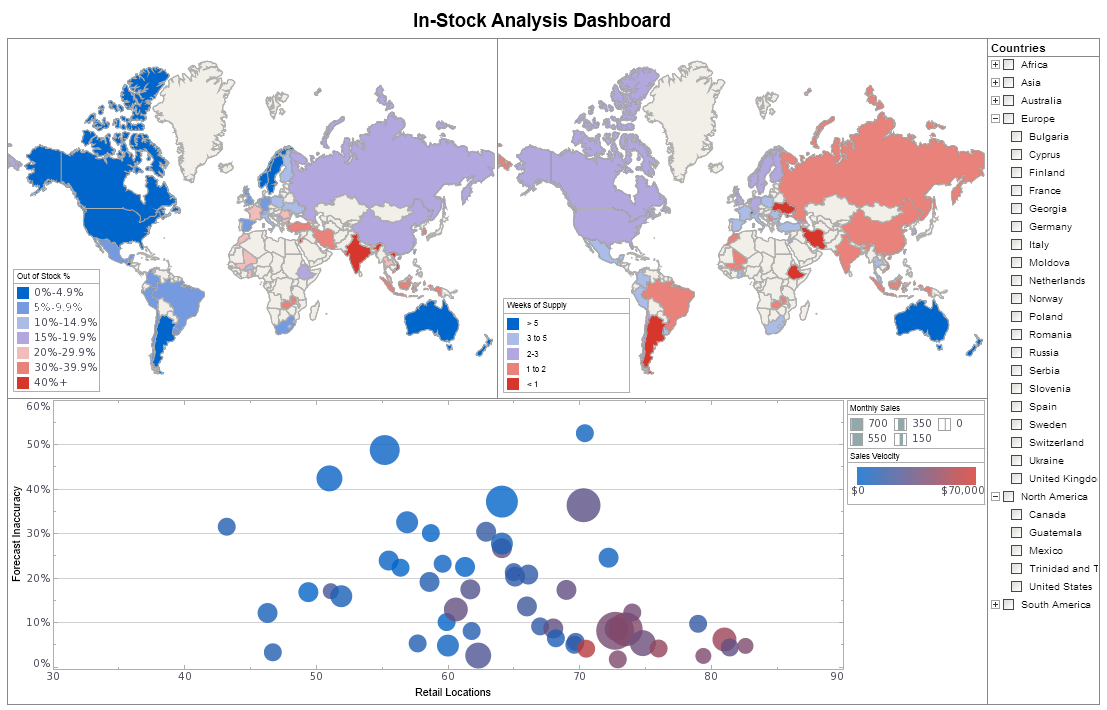
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
How Is Artificial Intelligence Used in Arbitrage Trading?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly transformed the landscape of arbitrage trading by enhancing the speed, efficiency, and accuracy of trading strategies. Here are some ways in which AI is utilized in arbitrage trading:
1. Market Analysis and Prediction
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of market data, including price movements, trading volumes, and historical trends, to predict future market behavior. Techniques such as machine learning and deep learning enable these systems to identify patterns and correlations that may indicate arbitrage opportunities.
2. High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
AI-powered high-frequency trading systems can execute trades at extremely high speeds, often within milliseconds. These systems can identify and capitalize on price discrepancies across different markets or financial instruments before human traders can react. The speed and precision of AI in HFT can significantly enhance the profitability of arbitrage strategies.
3. Sentiment Analysis
AI can process and analyze news articles, social media posts, and other text-based data sources to gauge market sentiment. Sentiment analysis algorithms can identify shifts in market mood that might influence asset prices, providing traders with early warnings of potential arbitrage opportunities.
4. Algorithmic Trading Strategies
AI systems can develop and implement complex algorithmic trading strategies that involve multiple trades across different assets and markets. These strategies can be backtested using historical data to ensure their effectiveness before being deployed in real-time trading.
5. Risk Management
AI can help manage risk by continuously monitoring market conditions and the performance of arbitrage strategies. Machine learning models can predict potential risks and adjust trading strategies accordingly to minimize losses and maximize profits. For instance, AI can automatically adjust the position sizes or set stop-loss orders based on real-time market data.
6. Execution Optimization
AI algorithms can optimize trade execution by choosing the best times and venues to execute trades, thus reducing transaction costs and minimizing market impact. These systems can dynamically adjust their strategies based on real-time market conditions to achieve the most favorable execution prices.
7. Market Making
In market making, AI algorithms can provide liquidity by simultaneously quoting buy and sell prices for financial instruments. By doing so, they can earn the spread between the bid and ask prices while balancing the inventory and minimizing risks. AI-driven market-making strategies can quickly adapt to market conditions, enhancing the efficiency and profitability of arbitrage trading.
8. Data Integration and Analysis
AI can integrate and analyze data from multiple sources, including financial markets, economic indicators, and alternative data sources such as satellite imagery or weather data. This comprehensive analysis can reveal hidden arbitrage opportunities that may not be apparent through traditional analysis methods.
9. Adaptive Learning and Evolutionary Algorithms
AI systems can employ adaptive learning techniques and evolutionary algorithms to continuously improve trading strategies. These algorithms can evolve by learning from past trades and market conditions, refining their approaches to enhance future performance.
10. Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI can detect unusual trading patterns and potential fraud by analyzing trading activities in real-time. This helps ensure the integrity of the trading environment and protects against market manipulation that could affect arbitrage opportunities.
Examples of AI in Arbitrage Trading
- Statistical Arbitrage: AI algorithms can identify statistical relationships between different securities and exploit deviations from historical correlations. For instance, if two stocks that typically move together start diverging, an AI system can execute trades to profit from their eventual convergence.
- Triangular Arbitrage: In the forex market, AI can monitor multiple currency pairs to identify and exploit discrepancies in exchange rates, executing simultaneous trades to lock in risk-free profits.
- Cross-Exchange Arbitrage: AI can track the prices of cryptocurrencies across different exchanges, identifying price differences and executing trades to profit from these discrepancies.
Significance of AI in Arbitrage Trading
- Speed and Efficiency: AI systems can process and analyze data much faster than humans, enabling quicker identification and execution of arbitrage opportunities.
- Accuracy: AI reduces the likelihood of human error, ensuring more precise execution of trades and better adherence to trading strategies.
- Scalability: AI-driven systems can handle large volumes of trades and data, making them suitable for high-frequency trading and other complex arbitrage strategies.
- Adaptability: AI can continuously learn and adapt to changing market conditions, improving the effectiveness of arbitrage strategies over time.
More Articles About Dashboard Reporting Usage
Artificial Neural Networks Inspiration - There are several different reasons to study how networks of neurons can compute things. The first is to understand how the brain actually works. You might think we could do just by experiments on the brain, but it's very big and complicated, and it dies when you poke around it too much...
Best Practices for Reviewing KPIs - This is business strategy. There will be a set of 5 or 6 KPIs that might never change. They should be part of the corporate culture. These reflect the company's goals. Here is what is important for my division. Here is what important for my role...
Changing Business Needs for BI - So organizations are now moving towards standardization of BI platforms and looking for a platform not just for the business intelligence needs but also to integrate it with business processes capabilities integrated with applications from multiple vendors and technologies such as search. That kind of standardization on one BI platform, it definitely helps to drive efficiency. The other area is to have service level agreements with the business...
Significance of a Modern Analytics Ecosystem - The foundation of well-informed decision-making is a contemporary analytics environment. Organizations generate insights that inform strategy development and tactical implementation by processing and analyzing data. Making judgments based on data lessens the need for intuition and guessing, resulting in decisions that are more effective and accurate...