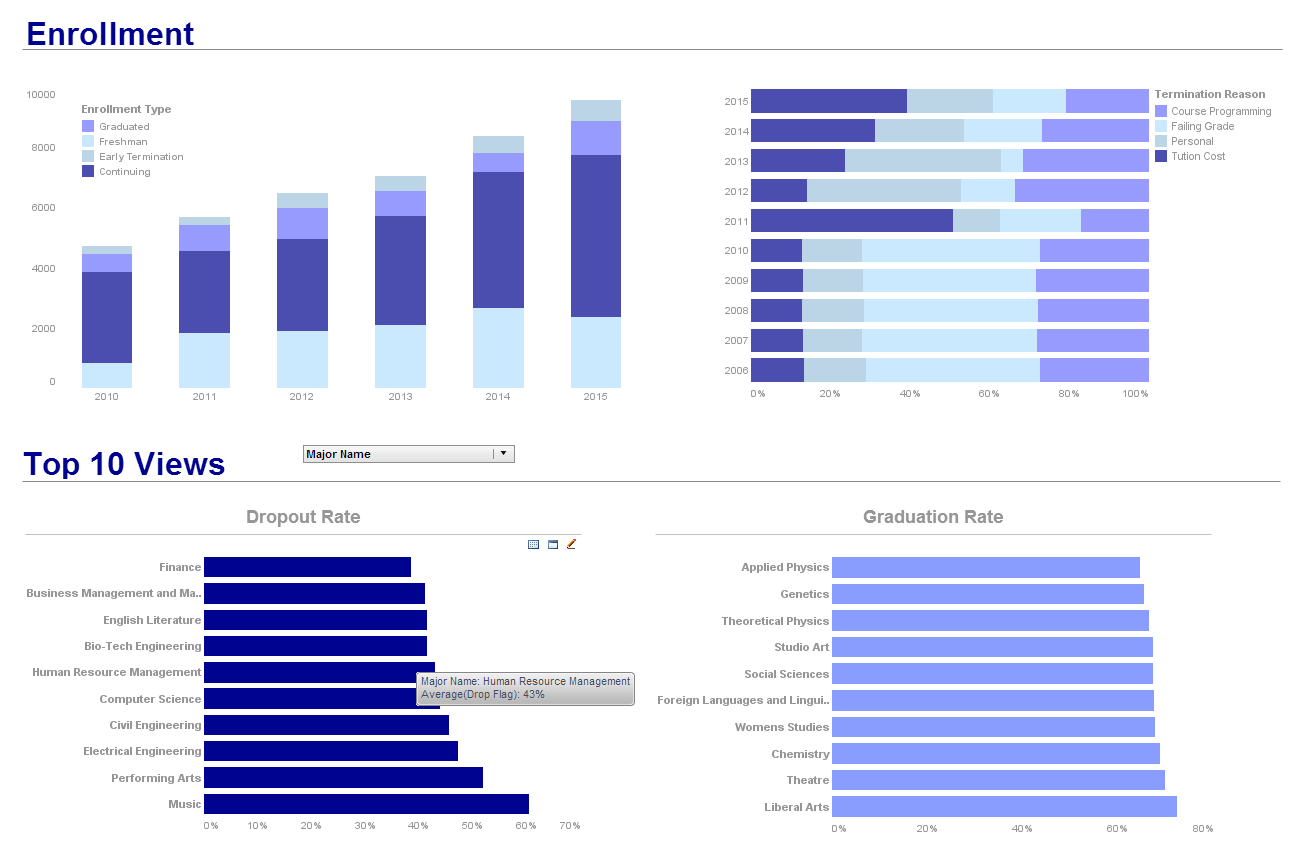
Download InetSoft's Data Visualization Software
Are you looking to download data visualization software? Since 1996 InetSoft has been making business software that is easy to deploy and easy to use. Build self-service oriented dashboards and visual analyses quickly. View a 3-minute demo and download a free version.
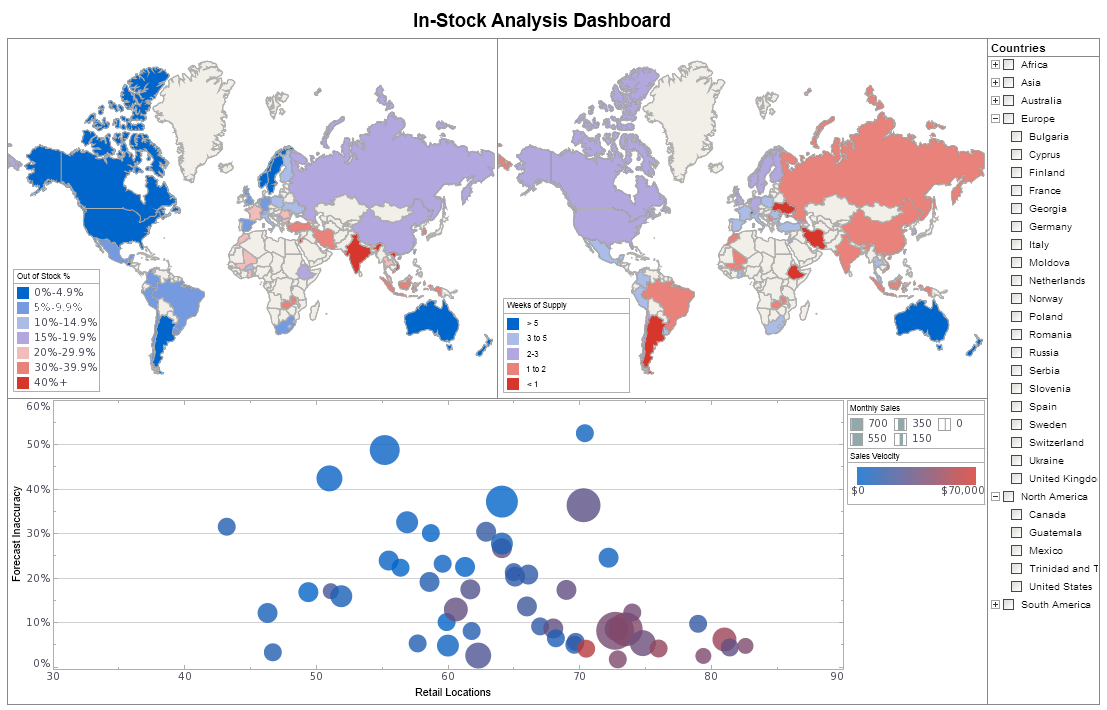
Why InetSoft?
InetSoft's data visualization application is easy enough to be:
- Deployed in just weeks
- Learned by end users with minimal training
- Used by any executive without the aid of IT
agile enough to be:
- Adaptable to changing data and business needs
- Used for data exploration through visualization
- Capable of maximum self-service
and robust enough to:
- Attract the attention of executives
- Meet the demands of power users
- Scale up for organizations of any size
Evaluate Style Scope from InetSoft. It's Easy. Agile. & Robust.
Register for more info and to download free eval software
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions. Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting. InetSoft's patent pending Data Block™ technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup.
This capability combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft's visual analysis technologies allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer. InetSoft was rated #1 in Butler Analytics Business Analytics Yearbook, and InetSoft's BI solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries.

What KPIs and Metrics Does the Broadcasting Industry Track with Data Visualization Software?
The broadcasting industry relies heavily on data visualization software to track and analyze various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics. These KPIs help broadcasters understand audience engagement, optimize content, manage operations, and drive profitability. Here are some essential KPIs and their definitions, along with their significance in performance management:
1. Audience Reach
- Definition: The total number of unique viewers or listeners who tune into a broadcast over a specific period.
- Significance: Indicates the size of the audience, which is critical for advertising revenue and market penetration.
2. Ratings and Shares
- Definition: Ratings measure the percentage of the total potential audience that is watching or listening to a broadcast, while shares measure the percentage of the audience actually consuming media at a given time.
- Significance: High ratings and shares reflect popular content and attract advertisers, essential for revenue generation.
3. Average Time Spent
- Definition: The average amount of time viewers or listeners spend on a broadcast.
- Significance: Longer viewing or listening times suggest engaging content and audience loyalty.
4. Peak Time Audience
- Definition: The highest number of viewers or listeners at any given time during a broadcast.
- Significance: Identifies the most popular segments or times, which can be targeted for premium advertising slots.
5. Ad Revenue
- Definition: The total income generated from advertising during broadcasts.
- Significance: Directly impacts the financial health of the broadcaster and guides content and scheduling decisions.
6. Cost per Thousand Impressions (CPM)
- Definition: The cost advertisers pay for 1,000 impressions of their ads.
- Significance: Helps broadcasters price their advertising slots competitively and maximize ad revenue.
7. Fill Rate
- Definition: The percentage of available ad slots that are sold.
- Significance: High fill rates indicate strong sales performance and effective inventory management.
8. Engagement Rate
- Definition: The level of interaction from the audience, including likes, shares, comments, and other forms of participation.
- Significance: Measures the effectiveness of content in capturing audience interest and encouraging interaction.
9. Churn Rate
- Definition: The percentage of viewers or subscribers who stop using the service over a given period.
- Significance: High churn rates indicate dissatisfaction and help identify areas for improvement in content or service quality.
10. Viewer Demographics
- Definition: The composition of the audience in terms of age, gender, location, income, etc.
- Significance: Understanding demographics helps tailor content and advertising to target audiences, improving engagement and ad effectiveness.
11. Content Performance
- Definition: Metrics that track how individual programs or segments perform, including ratings, engagement, and feedback.
- Significance: Identifies successful content and areas for improvement, guiding programming decisions.
12. Ad Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Definition: The percentage of viewers who click on an ad.
- Significance: High CTRs indicate effective ads that generate interest and potential sales, important for advertisers.
13. Subscription Growth Rate
- Definition: The rate at which new subscribers are added over a specific period.
- Significance: Indicates the success of marketing and promotional efforts and the overall appeal of the broadcast service.
14. Technical Quality Metrics
- Definition: Measures such as signal strength, broadcast interruptions, and error rates.
- Significance: Ensures high-quality broadcasts, reducing viewer frustration and maintaining audience loyalty.
15. Return on Investment (ROI)
- Definition: The profitability ratio calculated by dividing net profit by total investment.
- Significance: Indicates the financial success of broadcasting activities and helps guide investment decisions.
16. Social Media Mentions
- Definition: The number of times the broadcast or related content is mentioned on social media platforms.
- Significance: Reflects public interest and engagement, providing insights into audience preferences and content impact.
17. Mobile and Online Viewership
- Definition: The number of viewers accessing content through mobile devices and online platforms.
- Significance: Important for understanding multi-platform consumption patterns and expanding digital reach.
18. Viewer Retention Rate
- Definition: The percentage of viewers who return to watch subsequent episodes or broadcasts.
- Significance: Indicates the loyalty and satisfaction of the audience, essential for long-term success.
19. Program Costs
- Definition: The total expenses associated with producing and broadcasting a program.
- Significance: Helps in budgeting and evaluating the cost-effectiveness of content production.
20. Customer Support Metrics
- Definition: Metrics such as response time, resolution rate, and customer satisfaction with support services.
- Significance: Ensures high levels of viewer satisfaction and addresses any issues promptly, maintaining a positive relationship with the audience.
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
More Articles About Data Visualization Software
Align Your KPIs With Data Protection Goals - Tracking your KPIs provides insight into what's happening in your organization. Here are the ways to leverage them to your advantage. Before delving into the details of KPIs, it's important to ensure your organization has clear and defined data protection goals. These goals revolve around minimizing data breaches, improving response times to incidents, ensuring regulatory compliance, or enhancing overall data security. Once you have defined your data protection goals, the next step is to align your KPIs with these goals. The KPIs you select should serve as a metric to measure the performance and progress of your data protection strategies towards the set goals...
DMV Data Visualization - The State Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) relies heavily on data visualization for various purposes, including improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer service, ensuring regulatory compliance, and making data-driven decisions. Here are several ways in which the DMV utilizes data visualization: Traffic Management and Planning: By visualizing traffic patterns, congestion hotspots, and accident data, the DMV can collaborate with transportation authorities to optimize road infrastructure, plan new routes, and improve traffic flow...
More Options When Using Google Maps - When choosing the kind of map image to use in your data visualization, you have all of the options made available from the Google API. Google's documentation page details the options and URL fetching syntax, and highlights are mentioned here. Map size - the image file can be as large as 1280x1280 pixels under the free usage license, and 2048x2048 pixels under the commercial license...
Tracking Duty of Care for Travel Agencies - Duty of care refers to the legal and moral obligation that a company has to provide safety for their employees and protect them while working in remote places. To properly execute the duty of care, companies have to implement solutions for travel risk management. However, these measures, today, are not so much concerned with monitoring them and providing security. It is more about preparing the traveler by educating them about the trip...