Analytical Dashboard Vendor: InetSoft Technology
Are you looking for a good analytical dashboard vendor? Since 1996 InetSoft has been making BI software that is easy to deploy and easy to use. Build self-service oriented dashboards and visual analyses quickly. View a 3-minute demo and download a free version.
Why InetSoft?
InetSoft's analytic dashboard application is easy enough to be:- Deployed in just weeks
- Learned by end users with minimal training
- Used by any executive without the aid of IT
- Adaptable to changing data and business needs
- Used for data exploration through visualization
- Capable of maximum self-service
- Attract the attention of executives
- Meet the demands of power users
- Scale up for organizations of any size
Evaluate Style Scope from InetSoft. It's Easy. Agile. & Robust.
Register for more info and to download free eval software
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions. Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting. InetSoft's patent pending Data Block™ technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup.
This capability combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft's visual analysis technologies allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer. InetSoft was rated #1 in Butler Analytics Business Analytics Yearbook, and InetSoft's BI solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries.

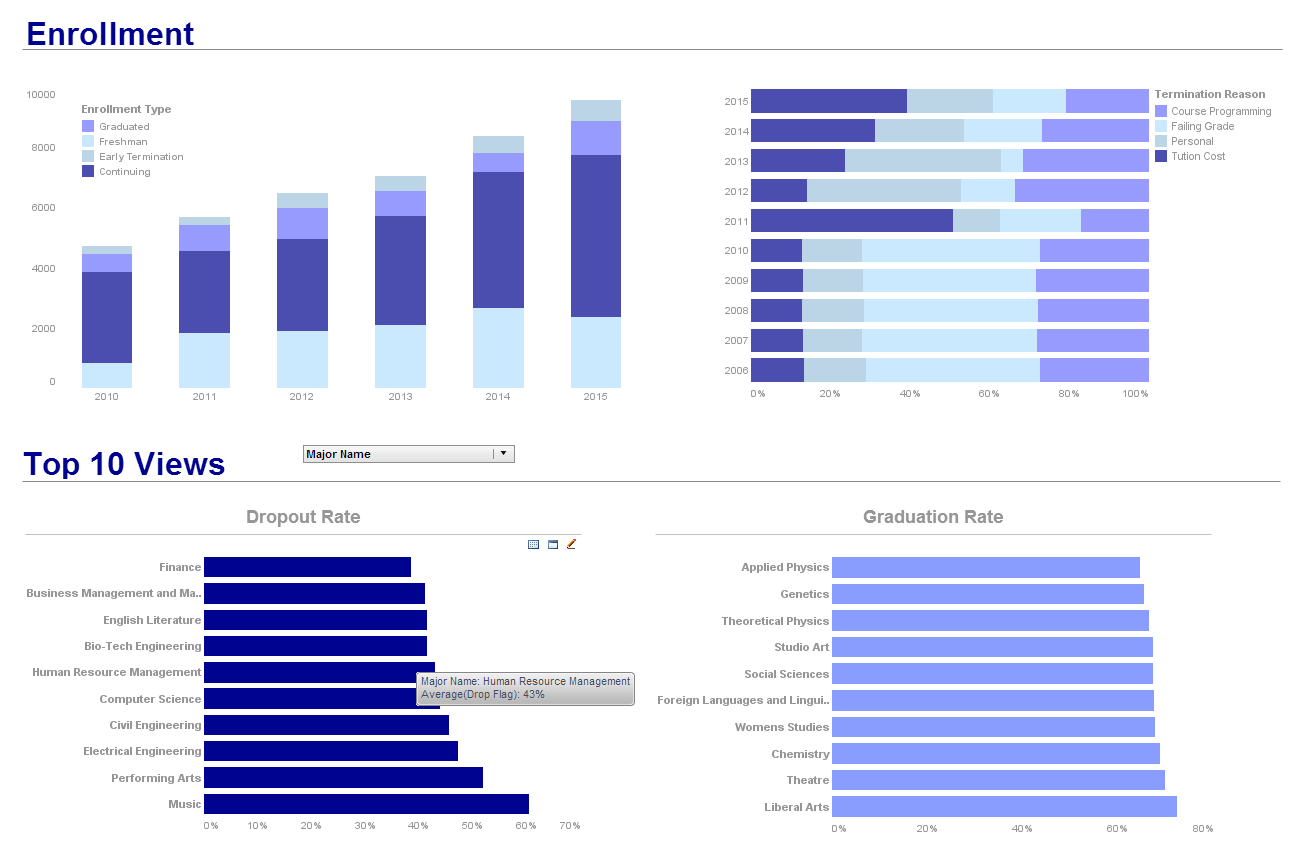
What KPIs and Metrics Are Tracked in Clinical Trials Management Dashboards?
Clinical trials management dashboards track a variety of KPIs and metrics to ensure the efficient and successful execution of clinical studies. These KPIs provide insights into the operational, financial, and clinical aspects of trials, helping stakeholders monitor progress, identify issues, and make informed decisions. Here are some key KPIs commonly tracked in clinical trials management dashboards:
1. Patient Recruitment Rate
- Definition: The number of patients recruited per unit of time (e.g., per month).
- Significance: A critical metric to ensure that the study can proceed on schedule. Slow recruitment can delay the trial and increase costs.
2. Patient Retention Rate
- Definition: The percentage of patients who remain in the trial until its completion.
- Significance: High retention is crucial for data integrity and the validity of trial results. High dropout rates can compromise the study's findings.
3. Enrollment Rate
- Definition: The percentage of the target patient population that has been enrolled in the trial.
- Significance: Indicates the progress towards achieving the enrollment target, which is essential for meeting timelines.
4. Screen Failure Rate
- Definition: The percentage of patients who fail the screening process and are not enrolled in the trial.
- Significance: High screen failure rates can indicate issues with the inclusion/exclusion criteria or the screening process itself.
5. Protocol Deviation Rate
- Definition: The number of deviations from the study protocol per 100 patients.
- Significance: Ensuring adherence to the protocol is vital for the validity and reliability of the trial data.
6. Data Query Resolution Time
- Definition: The average time taken to resolve data queries raised during the trial.
- Significance: Quick resolution of data queries ensures data quality and keeps the trial on schedule.
7. Site Activation Time
- Definition: The time taken to activate a trial site from the initiation visit to the first patient enrolled.
- Significance: Delays in site activation can push back the entire trial timeline. Efficient site activation is crucial for timely trial progress.
8. Adverse Event (AE) Reporting Rate
- Definition: The number of adverse events reported per 100 patients.
- Significance: Monitoring AEs is essential for patient safety and regulatory compliance. High rates may indicate issues with the intervention.
9. Serious Adverse Event (SAE) Rate
- Definition: The number of serious adverse events reported per 100 patients.
- Significance: SAEs are critical to monitor for patient safety and can impact the trial's continuation.
10. Protocol Compliance Rate
- Definition: The percentage of study visits and procedures conducted according to the protocol.
- Significance: High compliance ensures the reliability and integrity of trial data.
11. Study Timeline Adherence
- Definition: The percentage of study milestones met on time. Significance: Timely completion of milestones is essential for staying on schedule and within budget.
12. Budget Variance
- Definition: The difference between the planned and actual trial costs.
- Significance: Monitoring budget variance helps in controlling costs and ensuring the trial remains financially viable.
13. Patient Visit Compliance Rate
- Definition: The percentage of scheduled patient visits completed as planned.
- Significance: Ensures the collection of necessary data at the appropriate times, which is vital for the trial's success.
14. Data Entry Timeliness
- Definition: The average time from patient visit to data entry into the system.
- Significance: Timely data entry is crucial for real-time monitoring and decision-making.
15. Regulatory Submission Timeliness
- Definition: The percentage of regulatory submissions completed on or before the due date. Significance: Ensuring timely submissions helps avoid regulatory delays and potential fines.
16. Patient Demographic Diversity
- Definition: The distribution of enrolled patients across different demographic groups (age, gender, ethnicity).
- Significance: Ensuring diversity is important for the generalizability of trial results.
17. Monitoring Visit Frequency
- Definition: The average number of monitoring visits conducted per site per month.
- Significance: Regular monitoring ensures protocol adherence and data integrity.
18. Data Quality Metrics
- Definition: Various measures of data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Significance: High data quality is crucial for the credibility of trial outcomes.
19. Study Closeout Time
- Definition: The time taken to complete all activities after the last patient visit until the study is officially closed.
- Significance: Efficient closeout is important for timely reporting and regulatory compliance.
20. Investigator Satisfaction
- Definition: A measure of how satisfied investigators are with the support and resources provided during the trial.
- Significance: High satisfaction can improve site performance and encourage future collaboration
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
More Articles About Analytical Dashboards
Business Intelligence Strategy Scope - Now let's talk about the scope of BI strategy, and specifically one of the things I would like to lead off with is objectives. The objectives of your business intelligence initiative have got to be defined. So you have got to make sure of that in the beginning. You actually need to explain what are setting out to do. And I always encourage customers to have the objectives for the BI program be really in tune with the business strategy...
Tracking Bounce Rates for Explainer Videos - Bounce rate estimates the percentage of viewers who leave your content without taking any further action after watching the video. It indicates the level of engagement and interest of viewers beyond the video itself. A high bounce rate suggests that viewers don't find what they expected or desired after watching the video, leading them to leave without exploring other pages or performing additional actions. So, ensure that your video title and thumbnail represent the content...
Strategy for Self-service BI - And my last slide for this key issue is this notion of a cross-functional team that blends IT and business skills. It's just such a beautiful slide. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. Here you are seeing in this company, all the people with red circles around their head are from IT, all the people with blue circles around their heads are from the business...
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Using the Performance Scorecard - We have the strategy of using the performance scorecard, and we have all these things that are part of the design, including rules about how the design should evolve. I want to encourage people to become more innovative...
Vendor Management Metric: Vendor Risk Assessment - In order to detect possible risks related to suppliers, such as those related to their financial stability, regulatory compliance, data security, and business continuity planning, vendor management analysts undertake risk assessments. These evaluations aid in quantifying the vendor's risk exposure and serving as a roadmap for choosing amongst vendors...