A Cloud-Flexible Business Activity Monitoring Solution
Are you looking for a BI solution that offers effective business activity monitoring? InetSoft's software allows you to track the performance of any business function or department, from marketing lead generation to financial debit and credit transactions.
And with its powerful data mashup functionality, you can combine data from different functional areas to create a unified view of business activity.
Whether viewing a dashboard that display activity and lets you drill into reasons for ups and downs, or receiving alerts when performance falls below a threshold, InetSoft's easy-to-set up application keeps you on top of your business' activity at all times.
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
Advantages of StyleBI:
- Utilize existing data directly, realize immediate return on investment
- Gradually introduce more self-service without disruptions
- Share information among operational users, power users, and executives
- Yields Immediate ROI
- Carry a Lower Cost of Ownership
InetSoft technology provides the best software solution to suit any company's needs. StyleBI is...
robust enough to:
- build highly interactive and appealing dashboards
- tend to the needs of power users
- scale up for large organizations and their data sets
easy enough to be:
- deployed within weeks, not months
- utilized by business analysts, database admins, and even business users
flexible enough to:
- adapt to shifting data structures and extensive business needs
- allow maximum self-service through ad hoc and visual analysis
Read what InetSoft customers and partners have said about their selection of Style Scope for their solution for dashboard reporting. |
InetSoft's Interactive Reporting Tool
InetSoft's report designer is highly customizable providing the user with various viewing and reporting options.
InetSoft's comprehensive reporting platform can be used to create over 30 chart styles including bar, pie, line, curve, radar, waterfall, speedometer, pareto, candle, stock, stick, and bubble. These charts can be customized to show targets, provide desired x/y-axis formats and intervals, and even show multiple datasets.
IT professionals can create sophisticated production reports to be deployed for server-based, or desktop-based applications using StyleBI's reporting tool.
The small footprint and complete Java architecture makes it an ideal solution for embedded ad hoc reports.
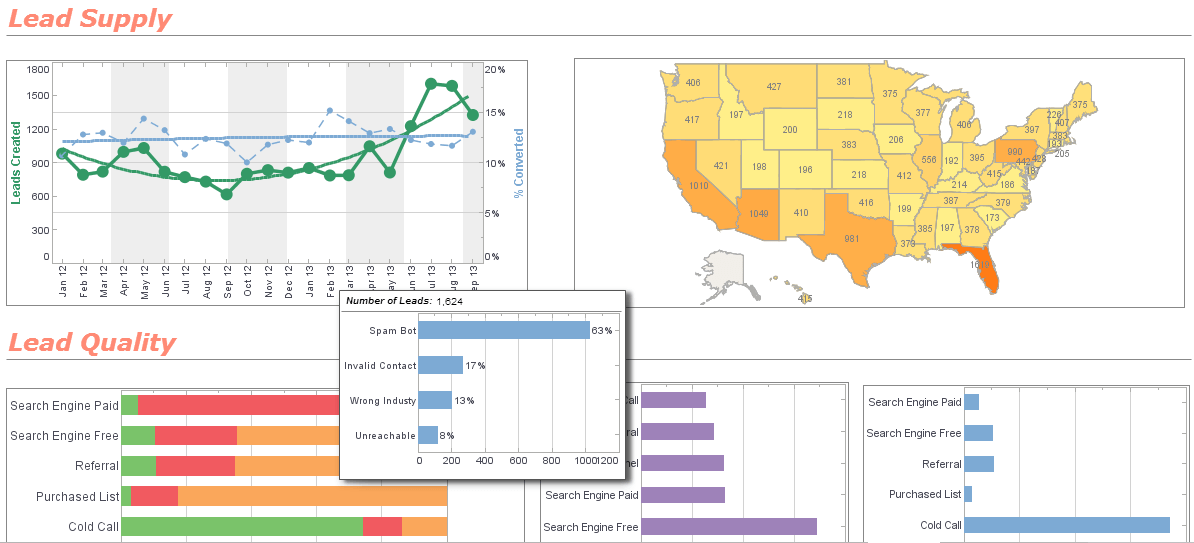
The image below shows an example of StyleBI's reporting capabilities.
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions.
Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting.
InetSoft's patent pending Data Block™ technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup. This capability combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft's visual analysis technologies allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer.
InetSoft solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries.
 |
Read the top 10 reasons for selecting InetSoft as your BI partner. |
How Does a Armament Manufacturer Use a Business Activity Monitoring Solution?
Armament manufacturers operate in a highly regulated and complex environment where precision, efficiency, and compliance are critical. Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) solutions play a vital role in helping these manufacturers manage their operations effectively. Here's how an armament manufacturer might use a BAM solution:
1. Real-Time Production Monitoring
- Operational Efficiency: BAM solutions provide real-time visibility into the production process, enabling manufacturers to monitor the status of machinery, production lines, and inventory levels. This ensures optimal utilization of resources and minimizes downtime.
- Quality Control: Continuous monitoring helps in detecting anomalies or deviations in the production process early. For example, if a machine starts producing parts that do not meet quality standards, the BAM system can trigger alerts for immediate corrective action.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Inventory Tracking: BAM solutions offer real-time tracking of raw materials and finished goods throughout the supply chain. This helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing storage costs, and preventing stockouts or overstock situations.
- Supplier Performance: Monitoring supplier deliveries and performance metrics ensures that materials are received on time and meet quality standards. This can include tracking delivery times, defect rates, and compliance with contractual agreements.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
- Documentation and Traceability: Armament manufacturers must comply with stringent regulatory requirements regarding documentation and traceability of products. BAM systems ensure that all production steps are logged and that documentation is readily available for audits and inspections.
- Compliance Monitoring: Real-time monitoring ensures that all processes adhere to industry regulations and internal policies. BAM solutions can generate compliance reports, making it easier to demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards.
4. Risk Management
- Incident Detection and Response: BAM solutions can detect potential risks or incidents, such as equipment malfunctions, safety breaches, or security threats, and trigger immediate responses to mitigate these risks.
- Predictive Maintenance: By monitoring equipment performance and using predictive analytics, BAM solutions can predict when maintenance is required, reducing the risk of unexpected failures and extending the lifespan of machinery.
5. Performance Analytics and Optimization
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): BAM systems track KPIs such as production rates, cycle times, yield rates, and downtime. This data helps in identifying areas for improvement and optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Operational Insights: Advanced analytics provide insights into production bottlenecks, process inefficiencies, and resource allocation. These insights enable manufacturers to make informed decisions to enhance productivity and reduce costs.
6. Security and Access Control
- Facility Monitoring: BAM solutions integrate with security systems to monitor access to facilities, ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter sensitive areas. This is crucial for maintaining the security of armament manufacturing operations.
- Data Security: Monitoring solutions track data access and usage, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
7. Project Management
- Milestone Tracking: For projects involving new armament development, BAM solutions track project milestones, timelines, and deliverables. This ensures that projects stay on schedule and within budget.
- Resource Allocation: Monitoring solutions help in allocating resources efficiently across various projects and departments, ensuring that critical tasks receive the necessary attention and support.
8. Customer Relationship Management
- Order Tracking: BAM systems monitor the status of customer orders in real-time, providing updates on production progress, expected delivery dates, and any potential delays.
- Quality Assurance: Monitoring customer feedback and product performance helps in maintaining high standards of quality and addressing any issues promptly, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
9. Cost Management
- Expense Tracking: BAM solutions provide real-time tracking of operational expenses, helping manufacturers manage costs effectively and identify areas for cost reduction.
- Budget Adherence: Monitoring financial performance against budgets ensures that projects and operations stay within financial constraints, improving overall financial management.
10. Innovation and Development
- R&D Monitoring: For ongoing research and development projects, BAM solutions track progress, resource utilization, and outcomes, facilitating innovation and continuous improvement.
- Prototype Testing: Monitoring the testing and evaluation of prototypes ensures that new products meet performance and safety standards before full-scale production.
Significance of BAM Solutions in Armament Manufacturing
- Enhanced Visibility: Real-time monitoring provides comprehensive visibility into all aspects of manufacturing operations, from production to supply chain and compliance.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights and analytics enable more informed and strategic decision-making, optimizing processes and improving overall efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: Early detection of issues and predictive maintenance reduce the risk of operational disruptions, ensuring smooth and continuous production.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automated documentation and reporting facilitate compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of penalties and enhancing reputation.
- Operational Efficiency: By identifying and addressing inefficiencies, BAM solutions help in improving productivity, reducing waste, and lowering costs.
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
What KPIs and Metrics Do Armament Manufacturers Track in the Manufacturing and Supply Processes?
Armament manufacturers, operating in a highly regulated and complex industry, track various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics to ensure efficiency, compliance, and quality throughout their manufacturing and supply processes. Below are some of the key KPIs and metrics, along with their definitions and significance in performance management:
1. Production Metrics
- Production Volume:
- Definition: The total number of units produced within a specific period.
- Significance: Measures the manufacturing output, helping to assess the capacity and efficiency of production processes.
- Cycle Time:
- Definition: The total time taken to produce one unit from start to finish.
- Significance: Identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the production line, enabling process optimization.
- Yield Rate:
- Definition: The percentage of products manufactured correctly without rework out of the total produced.
- Significance: Indicates the efficiency and quality of the production process. High yield rates signify effective production methods and fewer defects.
- First Pass Yield (FPY):
- Definition: The percentage of products that meet quality standards on the first attempt without any rework.
- Significance: Highlights the effectiveness of the production process and quality control. High FPY reduces costs and time associated with rework.
2. Quality Metrics
- Defect Rate:
- Definition: The number of defective units produced divided by the total number of units produced.
- Significance: Monitors the quality of production and helps identify areas requiring improvement.
- Cost of Quality (CoQ):
- Definition: The total cost associated with ensuring product quality, including prevention, appraisal, and failure costs.
- Significance: Helps in understanding the financial impact of quality management efforts and identifying areas where costs can be reduced.
- Non-Conformance Rate:
- Definition: The percentage of products that do not meet specified standards or requirements.
- Significance: A critical measure for maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations.
3. Supply Chain Metrics
- On-Time Delivery (OTD):
- Definition: The percentage of orders delivered on or before the agreed delivery date.
- Significance: Reflects the reliability and efficiency of the supply chain and manufacturing processes. High OTD rates indicate effective planning and logistics.
- Inventory Turnover:
- Definition: The ratio of the cost of goods sold to the average inventory level during a period.
- Significance: Measures how efficiently inventory is managed and how quickly products are sold or used. High turnover rates suggest efficient inventory management.
- Supplier Lead Time:
- Definition: The average time taken by suppliers to deliver materials after an order is placed.
- Significance: Helps in assessing supplier reliability and planning inventory levels to avoid production delays.
- Order Fulfillment Cycle Time:
- Definition: The total time taken from receiving a customer order to delivering the product.
- Significance: Indicates the efficiency of the entire order processing and delivery process. Shorter cycle times improve customer satisfaction.
4. Cost Metrics
- Manufacturing Cost per Unit:
- Definition: The total production cost divided by the number of units produced.
- Significance: Helps in determining the cost efficiency of the production process and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
- Direct Material Cost:
- Definition: The cost of raw materials used directly in the production of goods.
- Significance: Critical for budgeting and cost control, and helps in negotiating with suppliers.
- Operational Costs:
- Definition: The total costs associated with running the manufacturing operations, including labor, maintenance, and utilities.
- Significance: Monitors the overall financial health of the manufacturing operations and identifies areas for cost reduction.
5. Efficiency Metrics
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE):
- Definition: A composite measure of how effectively a manufacturing operation is utilized, calculated as Availability x Performance x Quality.
- Significance: Provides a comprehensive view of production efficiency and helps identify losses and areas for improvement.
- Utilization Rate:
- Definition: The percentage of available production capacity that is actually used.
- Significance: Helps in assessing whether manufacturing resources are being used efficiently and planning capacity expansions or reductions.
6. Safety and Compliance Metrics
- Incident Rate:
- Definition: The number of safety incidents per 100 employees over a specific period.
- Significance: Monitors workplace safety and helps in implementing measures to reduce accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
- Regulatory Compliance Rate:
- Definition: The percentage of operations and products that comply with relevant industry regulations and standards.
- Significance: Ensures adherence to legal and regulatory requirements, avoiding fines and reputational damage.
Significance in Performance Management
- Performance Optimization: Tracking these KPIs helps in identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement in manufacturing and supply processes, enabling continuous performance optimization.
- Quality Improvement: Quality metrics ensure that products meet high standards, reducing defects and rework, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Cost Control: Monitoring cost-related metrics helps in maintaining financial health, reducing waste, and improving profitability.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Supply chain metrics ensure that materials and products are delivered on time and inventory levels are optimized, supporting smooth production operations.
- Risk Management: Safety and compliance metrics help in managing risks, ensuring a safe working environment, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
- Strategic Decision-Making: These KPIs provide valuable data for strategic decision-making, helping managers to make informed choices about production planning, resource allocation, and process improvements.
More Articles on Business Activity Monitoring
Advantages of a NoSQL Distributed Database - Data processing software inspects, cleans, and transforms data, so that a decision maker can aggregate, chart and analyze the data to discover useful information, suggest conclusions, and expedite good decision making...
Cycle Time from Cash to Cash - This helps you to examine and keep track of how long it takes to turn resources into cash flows. Three ratios, the days of inventory, plus the days of payables, as well as the days of receivables, are combined in this KPI. It stands for the time elapsed between when a company pays cash to vendors and when it gets cash from customers. It is helpful when determining how much cash is required to fund continuing activities and is also known as the "cash conversion cycle...
Financial Enterprise Data Mashups - At InetSoft, we specialize in providing data mashups not only with your organizations financial data but also with your organizations large network of databases including, but not limited to: relational databases (JDBC), multidimensional databases, XML, SOAP, Java beans (POJO), EJB beans, flat files, Excel spreadsheets, OLAP cubes, and the proprietary data stores from JDE, SAP, PeopleSoft, and Siebel CRM...
Movie Production Companies and Big Data - Movie production companies have increasingly turned to big data in recent years to inform various aspects of the filmmaking process. This use of data helps them make more informed decisions, improve marketing strategies, enhance audience engagement, and ultimately increase the chances of a film's success. Here are several ways in which movie production companies leverage big data...