Try InetSoft's SQL Server Reporting Tool
Are you looking for a good reporting tool for SQL Server? Since 1996 InetSoft has been making reporting software that is easy to deploy and easy to use. Build self-service oriented interactive dashboards quickly. View a demo and read reviews.

Why InetSoft?
InetSoft's mobile BI reporting application is easy enough to be:
- Deployed in just weeks
- Learned by end users with minimal training
- Used by any executive without the aid of IT
agile enough to be:
- Adaptable to changing data and business needs
- Used for data exploration through visualization
- Capable of maximum self-service
and robust enough to:
- Attract the attention of executives
- Meet the demands of power users
- Scale up for organizations of any size
Evaluate StyleBI from InetSoft. It's Easy. Agile. & Robust.
Register for more info and free software software
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions. Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting. InetSoft's patent pending Data Block technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup.
This capability combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft's visual analysis technologies allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer. InetSoft was rated #1 in Butler Analytics Business Analytics Yearbook, and InetSoft's BI solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries.

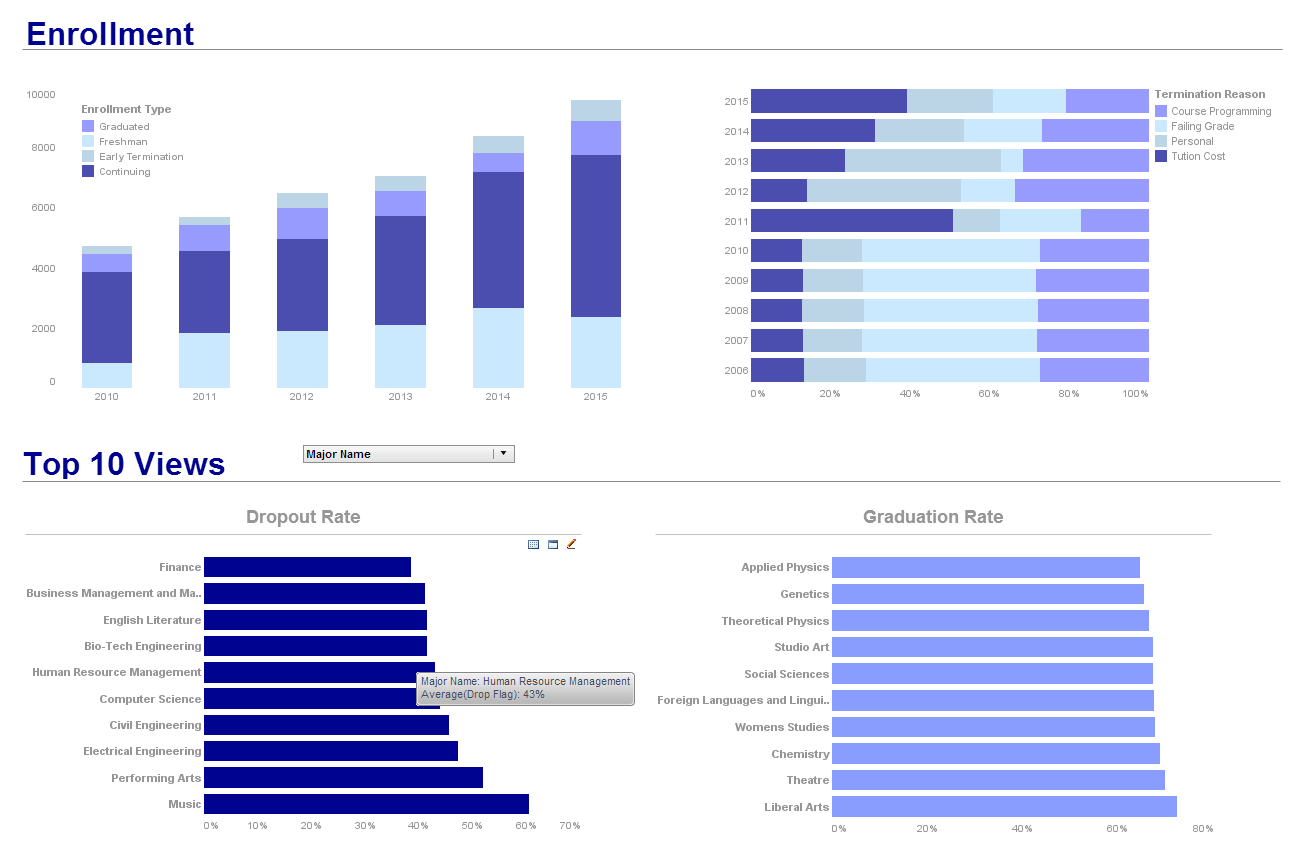
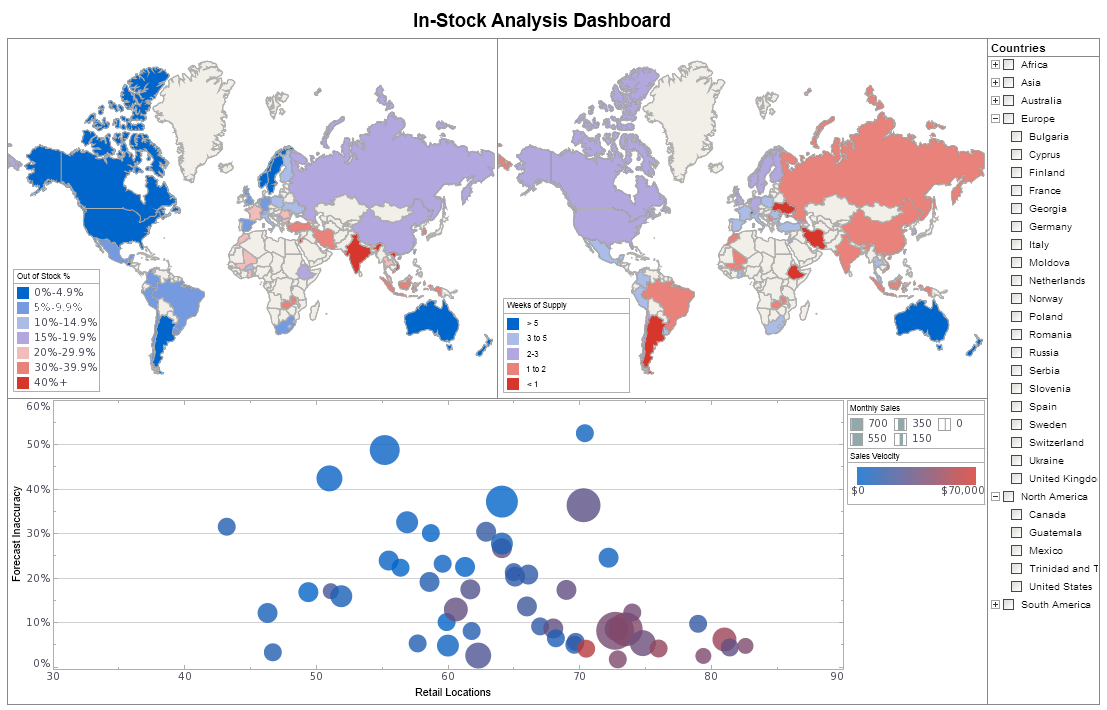
What KPIs and Metrics Are Tracked in Dashboards by Haulage Companies?
Haulage companies, which are involved in the transportation and delivery of goods, rely heavily on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics to monitor and improve their operations. Dashboards tracking these KPIs provide vital insights into various aspects of the business, from fleet efficiency to customer satisfaction. Below are some of the key KPIs and metrics tracked in haulage company dashboards, along with their definitions and significance in performance management.
1. Fleet Utilization
- Definition: The percentage of the fleet that is actively being used for transport operations at any given time.
- Significance: High fleet utilization indicates efficient use of resources. It helps in ensuring that the company is maximizing its assets and reducing idle time, which can be costly.
2. On-Time Delivery Rate
- Definition: The percentage of deliveries made on or before the scheduled delivery time.
- Significance: This metric is crucial for customer satisfaction and reliability. High on-time delivery rates build trust and repeat business with customers.
3. Fuel Efficiency
- Definition: The amount of fuel used per mile or per ton of goods transported.
- Significance: Monitoring fuel efficiency helps in managing fuel costs, which are a significant part of operating expenses. It also reflects on the environmental impact of the haulage operations.
4. Delivery Accuracy
- Definition: The percentage of deliveries that are completed without any errors, such as wrong items or quantities.
- Significance: High delivery accuracy minimizes customer complaints and returns, leading to better customer satisfaction and lower operational costs.
5. Average Delivery Time
- Definition: The average time taken to deliver goods from the point of dispatch to the destination.
- Significance: This metric helps in assessing the efficiency of the delivery process and identifying areas for improvement to reduce delivery times.
6. Maintenance Costs
- Definition: The total cost incurred for maintaining the fleet, including regular servicing and repairs.
- Significance: Keeping maintenance costs under control is essential for profitability. Regular maintenance also ensures vehicle safety and reliability.
7. Driver Performance
- Definition: Metrics related to driver behavior, such as speeding incidents, harsh braking, and adherence to routes.
- Significance: Monitoring driver performance can improve safety, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize wear and tear on vehicles. It also helps in training and incentivizing drivers.
8. Load Capacity Utilization
- Definition: The percentage of the vehicle's carrying capacity that is utilized on each trip.
- Significance: Efficient load capacity utilization ensures that each trip is cost-effective and maximizes the revenue potential of the haulage operations.
9. Customer Satisfaction
- Definition: Metrics derived from customer feedback, including satisfaction surveys and Net Promoter Score (NPS).
- Significance: High customer satisfaction is crucial for retaining clients and generating new business through positive referrals.
10. Cost per Mile
- Definition: The total operational cost divided by the number of miles driven.
- Significance: This metric helps in understanding the cost efficiency of the operations. Lowering the cost per mile can significantly improve profitability.
11. Revenue per Mile
- Definition: The total revenue generated divided by the number of miles driven.
- Significance: This metric helps in assessing the revenue efficiency of the haulage operations. Increasing revenue per mile indicates better pricing strategies and route optimization.
12. Order Cycle Time
- Definition: The total time from receiving an order to its final delivery.
- Significance: Shorter order cycle times improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. It helps in identifying bottlenecks in the process that can be optimized.
13. Idle Time
- Definition: The amount of time vehicles are not in use or drivers are not working, excluding breaks.
- Significance: Reducing idle time increases productivity and ensures that assets and human resources are being used efficiently.
14. Accident Rate
- Definition: The number of accidents per mile driven or per number of deliveries made.
- Significance: Lower accident rates reflect better safety practices and reduce costs related to damages, insurance, and potential legal issues.
15. Compliance Rate
- Definition: The percentage of operations that meet regulatory and safety compliance standards.
- Significance: High compliance rates minimize the risk of legal penalties and enhance the company's reputation for reliability and safety.
16. Freight Claims Rate
- Definition: The percentage of deliveries that result in freight claims due to damage or loss.
- Significance: Lower freight claims rates indicate better handling and transportation practices, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced costs.
17. Operational Efficiency
- Definition: A composite metric that includes various factors such as on-time deliveries, fuel efficiency, and cost per mile.
- Significance: This provides a holistic view of the overall efficiency of the haulage operations and helps in benchmarking performance against industry standards.
18. Environmental Impact Metrics
- Definition: Metrics such as carbon emissions per mile or per ton of goods transported.
- Significance: Reducing environmental impact is increasingly important for regulatory compliance and corporate social responsibility. It also appeals to environmentally conscious customers.
19. Warehouse Turnaround Time
- Definition: The time taken to load or unload goods at the warehouse.
- Significance: Faster turnaround times improve the overall efficiency of the delivery process and reduce vehicle downtime.
20. Route Optimization Metrics
- Definition: Metrics related to the efficiency of the routes taken, including average distance traveled and time spent on the road.
- Significance: Optimized routes reduce fuel consumption, travel time, and operational costs, leading to more efficient and cost-effective haulage operations.
Significance in Performance Management
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Tracking KPIs such as fleet utilization, load capacity utilization, and operational efficiency helps in identifying inefficiencies in the haulage operations. By monitoring these metrics, managers can make informed decisions to optimize routes, reduce idle times, and ensure that vehicles are used to their maximum potential.
Cost Management
Metrics like cost per mile, fuel efficiency, and maintenance costs are critical for managing the financial aspects of the business. By keeping these costs under control, haulage companies can improve their profitability and competitiveness. For instance, improving fuel efficiency through better driver training and vehicle maintenance can significantly reduce operational costs.
Quality Assurance and Customer Satisfaction
KPIs such as on-time delivery rate, delivery accuracy, and customer satisfaction are directly linked to the quality of service provided. High performance in these areas ensures that customers are happy with the services, leading to repeat business and positive referrals. Monitoring these metrics also helps in identifying areas where the service quality can be improved.
Safety and Compliance
Safety is a paramount concern in the haulage industry. Metrics like accident rate, driver performance, and compliance rate are essential for maintaining high safety standards. Reducing accidents not only protects the drivers and the public but also reduces costs related to damages and insurance. Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards minimizes the risk of legal penalties and enhances the company's reputation.
Strategic Planning
Metrics such as forecast accuracy, environmental impact, and route optimization support long-term strategic planning. Accurate demand forecasts help in planning the fleet and resources efficiently, while environmental impact metrics align operations with sustainability goals. Route optimization ensures that the most efficient and cost-effective routes are used, reducing overall costs and improving service delivery times.
Continuous Improvement
Regular monitoring and analysis of these KPIs allow for continuous improvement in haulage operations. By identifying trends and patterns, managers can implement data-driven strategies to enhance performance. For example, if the on-time delivery rate is lower than desired, analyzing the root causes can lead to process improvements and better scheduling practices.
More Articles About SQL Server Reporting Tools
Car Manufacturing Data Visualization - Production Monitoring and Control: Data visualization tools are used to monitor and visualize real-time data from the production line. Managers and operators can track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production rates, defect rates, machine utilization, and downtime. Visualizing this data helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and potential issues, allowing for prompt action and process improvements...
Evaluate InetSoft's Monthly Report Tool This Year - Are you looking for the best monthly report tools? InetSoft's pioneering dashboard reporting application produces great-looking web-based or paginated reports. The software has been top rated by customers for personalized support on G2. View a demo and try interactive examples...
Heavy Construction Project Progress Tracking - Following a construction project's development is essential to guaranteeing its timely completion and resource efficiency. Dashboards for heavy construction software include KPIs that provide current information on the status of projects. Important measurements consist of: Completion Percentage: This KPI gives an overview of the project's current status in relation to its whole scope. It helps project managers determine if the work is progressing according to plan...
Validation of BI Requirements - And so in order for them to a qualify and make certain of their requirements are sound before they send them out to tender, they need some sort of validation process.Some of the contracting officers we talk to say that we have selection criteria, and it's largely based on a dollar value, but there is a huge initiative within the federal government to say we're trying to evaluate this is not only based on value, but quality of services and quality of requirements and quality of goods procured...
