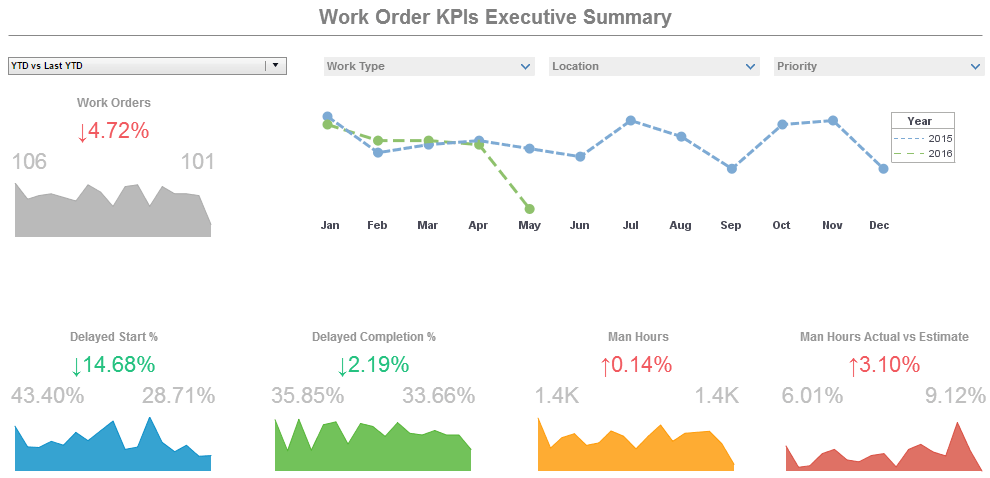
Work Order KPI Dashboard
The larger a company becomes the harder it is to manage work orders and ensure preventative maintenance is carried out. With InetSoft end users can create visualization and reporting solutions utilizing robust data mashup and unlimited data connectivity which supplements or obviates the need for IT-intensive ETL and data warehouses.
The example dashboard provided was created utilizing StyleBI, InetSofts flagship data intelligence platform. This highly visual and interactive display allows executives to view all the necessary key performance indicators for tracking and managing work orders.
In this hypothetical situation the executive can see that work orders have gone down while man hours have gone up. The drop down bars at the top are critical since it allows the executive to filter information based on date, work type, location, and priority.
KPIs and Metrics Tracked in Work Order Dashboards: Definitions and Significance in Performance Management
- Work Order Completion Rate
- Definition: The percentage of work orders completed within a given time frame compared to the total number of work orders issued.
- Significance: This KPI measures the efficiency of the maintenance or service team. A high completion rate indicates effective workflow management and resource allocation. It also reflects the team's ability to meet deadlines and maintain operational continuity.
- Average Time to Complete a Work Order
- Definition: The average duration from the initiation to the completion of a work order.
- Significance: This metric helps in identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the work order process. A shorter average time suggests streamlined processes and effective task prioritization. Conversely, longer times may indicate issues that require attention, such as resource shortages or process inefficiencies.
- First-Time Fix Rate
- Definition: The percentage of work orders resolved on the first attempt without the need for follow-up actions.
- Significance: A high first-time fix rate is a critical indicator of the quality and effectiveness of the maintenance or service team. It reflects the team's competency and the adequacy of initial problem assessments. High rates reduce downtime and improve customer satisfaction.
- Backlog of Work Orders
- Definition: The total number of work orders that are pending and have not yet been completed.
- Significance: Managing backlog is crucial for maintaining workflow efficiency. A large backlog can indicate resource constraints, process inefficiencies, or scheduling issues. Keeping the backlog at manageable levels ensures timely attention to work orders and prevents delays in operations.
- Maintenance Cost per Work Order
- Definition: The average cost incurred to complete a work order.
- Significance: This metric is essential for budget management and cost control. By tracking maintenance costs, organizations can identify areas where expenses can be reduced without compromising quality. It also aids in financial planning and resource allocation.
- Work Order Priority Levels
- Definition: The categorization of work orders based on their urgency and importance (e.g., high, medium, low).
- Significance: Prioritization ensures that critical tasks are addressed promptly, thereby preventing potential disruptions. Tracking priority levels helps in effective resource allocation and ensures that high-priority tasks receive the necessary attention.
- Response Time to Work Order Requests
- Definition: The time taken from the submission of a work order request to the commencement of work.
- Significance: Quick response times are indicative of efficient request handling and resource availability. This metric is crucial for maintaining service levels and customer satisfaction, particularly in industries where prompt attention to issues is essential.
- Scheduled vs. Unscheduled Work Orders
- Definition: The ratio of planned (scheduled) maintenance tasks to unplanned (unscheduled) tasks.
- Significance: A higher proportion of scheduled work orders indicates proactive maintenance practices, which can prevent unexpected breakdowns and reduce downtime. This metric helps in assessing the effectiveness of maintenance planning and preventive measures.
- Work Order Rework Rate
- Definition: The percentage of work orders that require rework or additional corrections after initial completion.
- Significance: A high rework rate can signify underlying issues such as inadequate initial problem assessment, poor-quality workmanship, or insufficient training. Reducing rework rates improves efficiency and reduces costs.
- Technician Utilization Rate
- Definition: The percentage of time that technicians are actively engaged in completing work orders compared to their total available working hours.
- Significance: High technician utilization rates indicate optimal use of human resources. This metric helps in workforce planning and can highlight areas where additional training or hiring may be necessary.
The Significance of KPIs in Performance Management
KPIs and metrics in work order dashboards play a crucial role in performance management by providing actionable insights that drive continuous improvement. Here are some key ways in which they contribute to performance management:
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: KPIs offer quantifiable data that support informed decision-making. Managers can identify trends, analyze performance, and make strategic adjustments based on real-time data. This data-driven approach minimizes guesswork and enhances operational efficiency.
-
Improved Resource Allocation: By monitoring KPIs such as technician utilization rates and work order backlog, organizations can optimize resource allocation. This ensures that personnel and equipment are used effectively, reducing idle time and improving productivity.
-
Increased Accountability: KPIs create a framework for accountability by setting clear performance benchmarks. Employees and teams are aware of their performance expectations and can be held accountable for meeting these standards. This promotes a culture of responsibility and continuous improvement.
-
Proactive Maintenance: Tracking metrics like scheduled vs. unscheduled work orders and maintenance cost per work order encourages proactive maintenance strategies. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and extends the lifespan of equipment, ultimately lowering maintenance costs.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Metrics such as response time to work order requests and first-time fix rate directly impact customer satisfaction. Prompt and effective resolution of issues leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, which is particularly important in service-oriented industries.
-
Cost Management: Monitoring maintenance costs per work order and overall maintenance expenses helps in controlling costs and improving budget management. Organizations can identify cost-saving opportunities and implement measures to reduce unnecessary expenses without compromising service quality.
-
Performance Benchmarking: KPIs allow organizations to benchmark their performance against industry standards or competitors. This comparative analysis helps in identifying areas of improvement and adopting best practices to enhance overall performance.
-
Trend Analysis and Forecasting: Regular tracking of KPIs enables trend analysis and forecasting. Organizations can identify seasonal variations, recurring issues, and long-term trends that inform future planning and strategy development.
-
Continuous Improvement: KPIs provide a basis for continuous improvement initiatives. By regularly reviewing and analyzing performance metrics, organizations can implement targeted improvements, streamline processes, and achieve higher efficiency.

Prevent Profit Loss and Increase Work Orders and Employee Efficiency
InetSoft is a pioneer in data mashup and allows disparate data sources of almost any type to be combined in order to produce reports and dashboards that provide new insights. These interactive dashboards create internal information management efficiencies because it is usable by all levels of employees. This is all done in a web based interface utilizing drag-and-drop features that makes it possible for the everyday user to make complex dashboards without the need for programming experience thus freeing up time and costs. Try online for free by clicking the orange button to the left.
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions. Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting. InetSoft’s patent pending Data Block™ technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup.
This capability, combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft’s visual analysis technologies, allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer. InetSoft solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries

More Articles About Work Dashboards
Claims and Damage Control Claim Rate - This KPI calculates the proportion of shipments that generate claims for theft, loss, or damage. Analysis of claim rates reveals possibilities for improvement in risk management, handling, and packing procedures...
Data Integration and Pervasive BI - It certainly simplifies and it makes it more possible to become pervasive. InetSoft's unique data mashup engine allows combinations of almost any data source into a common BI infrastructure so you can make dashboards and reports that previously had to be done manually in a spreadsheet, for instance...
Data Intelligence for Trading Firms -Today, the pendulum has swung in the Buy-side's favor. Time-honored personal relationships no longer guarantee orders for Sell-side banks. As newer electronic trading channels have opened and emerged, the Buy-side bank no longer needs personal contact with the Sell-side bank to handle a trade. The net result: personal relationships are not enough to guarantee an order...
Government Data Is Huge - The data the government has is so huge. It dwarfs what you see on the commercial side. So you talk about big data. Well, the government has huge data. The government is massive. They are big generators of data. They are big compilers of data that has been used in the commercial word for research, for making policy decisions within the government. So there is so much that is being done and can be done by getting that information in the hands of the people that need to make the right decisions...
Incident Volume and Trends - The number and patterns of incidents must be monitored for effective incident management. By highlighting incident frequency over a certain time frame, this KPI enables companies to see trends and probable causes of recurrent problems. Businesses may efficiently allocate resources, identify areas of risk, and put preventative measures in place by monitoring incident volume and patterns. This KPI aids firms in ensuring that incident management initiatives are in line with corporate goals...