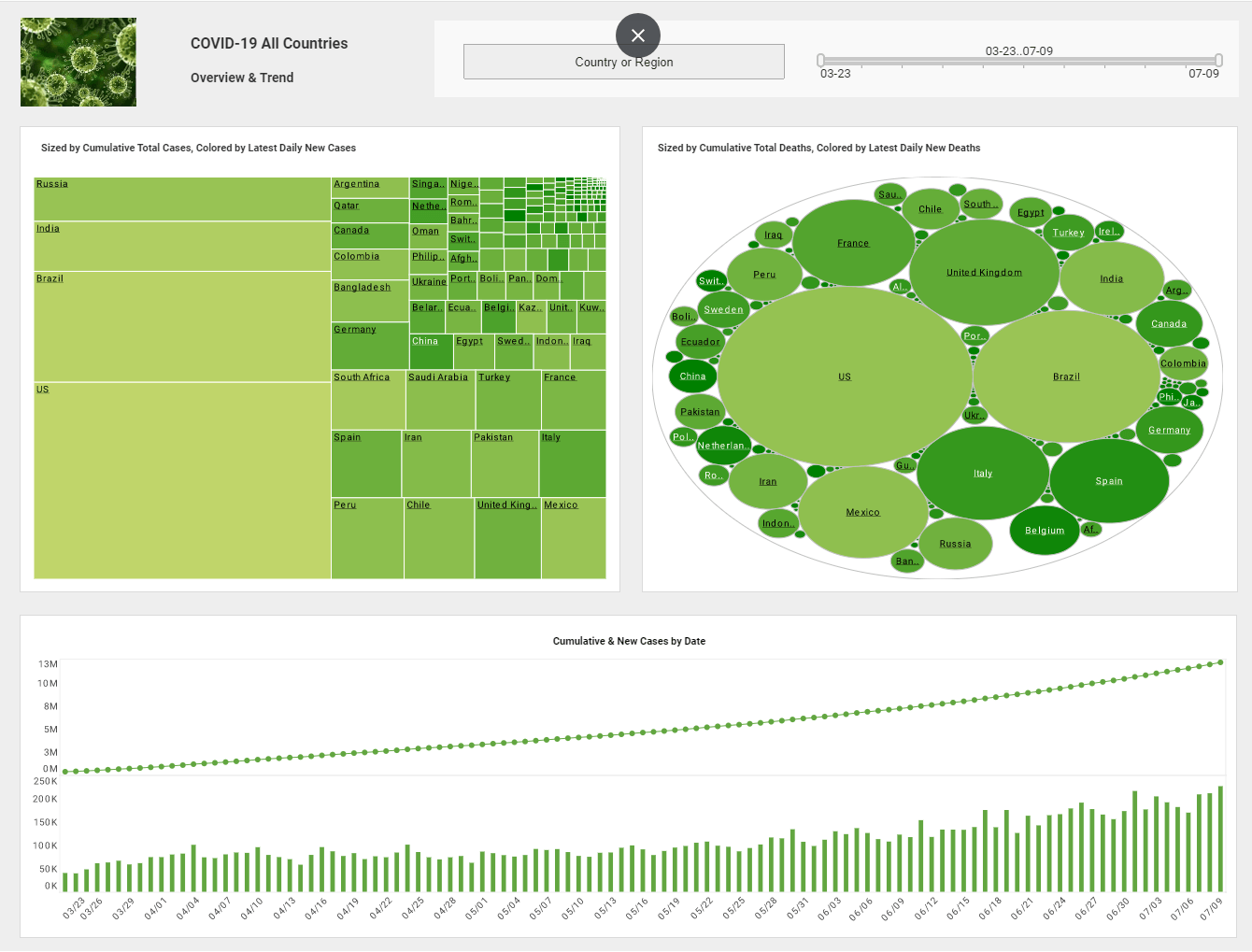
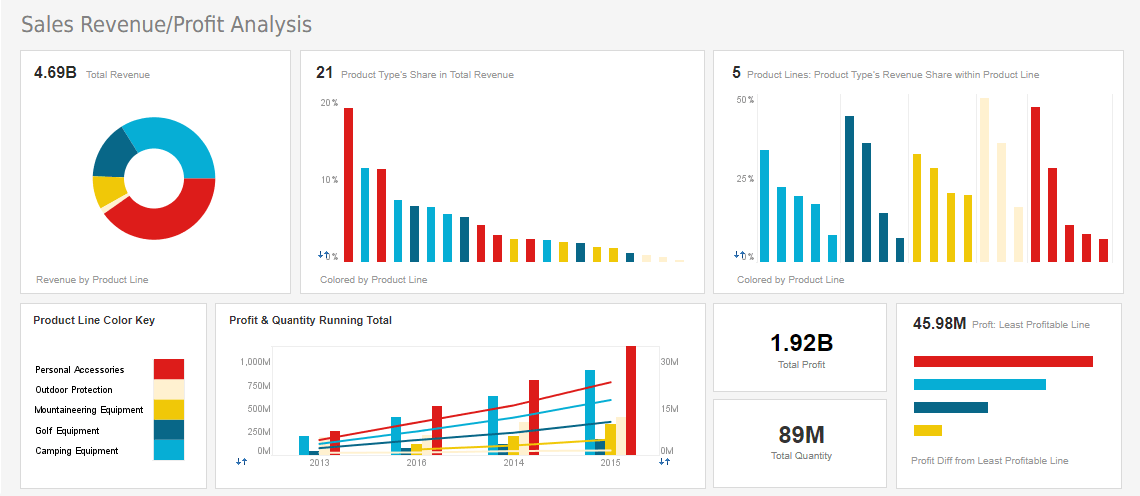
InetSoft Viewpoint
"Is performance management expensive? There clearly are expenses associated with it. It’s not so
much the technology. Good systems can be bought for tens of thousands of dollars. They don’t have to be
hundreds of thousands of dollars. But what’s the cost associated with how you do things? Or how you look
at things?
The benefits are pretty extraordinary if you crack the code on that. Performance management really shines you
have a C-level executive, whether it be the CFO or the CEO, or in some instances, the CIO. But typically
it’s the either the CEO or the CFO who have vision for performance management. They realize that they
need to do things differently. And not just for things like compliance, but for real transparency. Then things
can start to happen.
Part of the challenge with performance management is that sometimes it gets hung up in the department of
finance, yet it really applies more broadly in the enterprise. Most organizations haven’t gotten there,
yet. Some have applied it to operations. Some have gone beyond just the financial indicators of an
organization. So that’s a big thing being able to do that, but also being able to reconcile the
information, or the way you manage the business, the way that we report things, that’s another
challenge." - Mark Flaherty, CMO, InetSoft
“Flexible product with great training and support. The product has been very useful for quickly creating dashboards and data views. Support and training has always been available to us and quick to respond.
- George R, Information Technology Specialist at Sonepar USA
What Has changed in BI Design Philosophy?
Over the last five years, the design philosophy of business intelligence (BI) has evolved significantly,
driven by technological advancements and shifting user expectations. One major change has been the shift
towards self-service BI. Modern BI tools are designed to empower end-users, allowing them to access, analyze,
and visualize data without relying heavily on IT departments. This democratization of data has led to a more
agile and responsive decision-making process within organizations, enabling users at all levels to derive
insights and take action swiftly.
Another transformative trend has been the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning
(ML) into BI platforms. These technologies have enhanced the capabilities of BI tools, allowing for predictive
analytics, anomaly detection, and automated insights. Instead of merely presenting historical data, modern BI
solutions can now forecast future trends, identify outliers, and even suggest actions based on data patterns.
This shift has made BI not just a tool for reporting but a proactive system for strategic planning and
operational optimization.
The rise of cloud computing has also played a crucial role in reshaping BI design philosophy. Cloud-based BI
solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency that on-premises systems cannot match. With
cloud BI, organizations can handle vast amounts of data, perform complex analyses, and collaborate across
geographies seamlessly. This shift to the cloud has facilitated real-time data processing and analytics,
ensuring that decision-makers have access to up-to-date information whenever and wherever they need it.
User experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design have become central to BI development in recent years.
The focus has shifted from just functionality to creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that enhance the
overall experience. Modern BI tools emphasize ease of use, with drag-and-drop interfaces, customizable
dashboards, and interactive visualizations. This focus on UX/UI design ensures that even non-technical users
can navigate and utilize BI tools effectively, driving broader adoption and better data-driven decision-making
across organizations.
Lastly, the importance of data governance and security in BI design has surged, reflecting the growing
concerns over data privacy and regulatory compliance. Modern BI platforms are now built with robust security
features, including data encryption, user authentication, and access controls. Additionally, they support
comprehensive data governance frameworks that ensure data integrity, consistency, and traceability. This
heightened focus on security and governance ensures that organizations can trust their data and comply with
regulatory requirements, mitigating risks associated with data breaches and non-compliance.