InetSoft's Business Intelligence Software: Easy, Agile, and Robust
InetSoft's business intelligence software features dashboards, analysis, and reporting that is easy, agile, and robust.
InetSoft's flagship product, Style Intelligence™, goes beyond traditional business intelligence by providing a complete BI software platform that includes fine-grained security and administration for accessing diverse data sources.
In addition to pixel-perfect report publication, this advanced BI platform offers powerful yet easy-to-use Web-based applications for dashboard creation and interactive visual analysis.
Case Study: National Institutes of Health Utilizing Business Intelligence Software
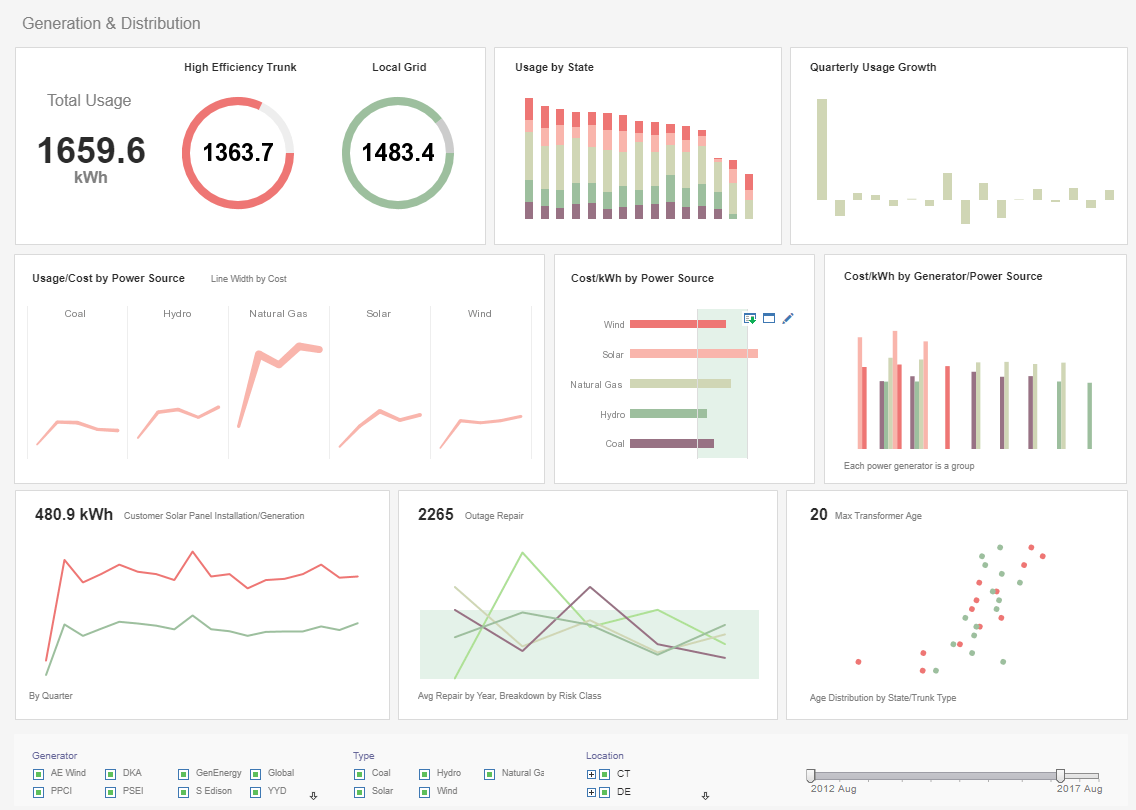
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is a leading biomedical research institution, tasked with advancing knowledge and improving health outcomes through research. With a vast amount of data generated from research projects, grants, and clinical trials, the NIH recognized the need for a robust Business Intelligence (BI) software solution to manage, analyze, and derive actionable insights from their data. This case study explores the implementation of BI software at the NIH, detailing the process, challenges, and outcomes.
Background
The NIH operates numerous research programs and manages extensive datasets, including clinical trial results, research funding allocations, and publication records. Traditional data management methods were inadequate for handling the volume and complexity of NIH's data, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities for insights. To address these issues, the NIH decided to implement a comprehensive BI software solution to enhance data analysis capabilities, streamline reporting, and support evidence-based decision-making.
Implementation of Business Intelligence Software
Objectives
The primary objectives of implementing BI software at the NIH were:
- To centralize and streamline data management across various departments.
- To enhance data analysis capabilities for more informed decision-making.
- To improve reporting efficiency and accuracy.
- To enable real-time data visualization and insights.
Key Steps in Implementation
- Needs Assessment and Planning:
- Conducting a thorough assessment of NIH's data management needs, existing systems, and analytical capabilities.
- Defining the scope, goals, and expected outcomes of the BI software implementation.
- Vendor Selection:
- Evaluating various BI software vendors based on criteria such as functionality, scalability, user-friendliness, and cost.
- Selecting a BI software solution that best met NIH's requirements.
- Data Integration:
- Integrating data from multiple sources, including research databases, grant management systems, and clinical trial records, into the BI platform.
- Ensuring data quality and consistency through data cleansing and standardization processes.
- Customization and Development:
- Customizing the BI software to meet NIH's specific needs, including the development of tailored dashboards, reports, and analytics tools.
- Collaborating with stakeholders to ensure the BI solution aligns with their requirements and expectations.
- Training and Change Management:
- Providing comprehensive training programs for NIH staff on how to use the new BI software effectively.
- Implementing change management strategies to facilitate smooth adoption and integration of the BI solution into daily operations.
- Pilot Testing and Scaling:
- Launching pilot projects to test the BI software's functionality and identify any issues or areas for improvement.
- Gradually scaling the implementation to include all relevant departments and research programs.
Challenges and Solutions
Challenges
- Data Integration Complexity:
- Integrating diverse datasets from multiple sources posed significant technical challenges.
- User Adoption:
- Ensuring staff across different departments adopted and effectively used the new BI software required considerable effort.
- Data Security and Privacy:
- Handling sensitive research data and ensuring compliance with data security and privacy regulations was critical.
Solutions
- Robust Data Integration Framework:
- Developing a robust data integration framework to seamlessly aggregate data from various sources.
- Utilizing data cleansing and transformation tools to ensure data quality and consistency.
- Comprehensive Training Programs:
- Conducting extensive training sessions and providing ongoing support to help users become proficient with the BI software.
- Creating user-friendly guides and resources to facilitate self-learning.
- Enhanced Security Measures:
- Implementing advanced security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, to protect sensitive data.
- Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations through strict data governance policies.
Outcomes and Benefits
The implementation of BI software at the NIH resulted in several significant outcomes and benefits:
- Improved Data Management:
- Centralized data management streamlined data collection, storage, and retrieval processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing redundancy.
- Enhanced Analytical Capabilities:
- Advanced analytics tools enabled NIH researchers and administrators to derive deeper insights from their data, supporting evidence-based decision-making.
- Streamlined Reporting:
- Automated reporting features reduced the time and effort required to generate accurate and timely reports, improving operational efficiency.
- Real-Time Data Visualization:
- Interactive dashboards and real-time data visualization tools provided NIH stakeholders with instant access to critical information, facilitating quick and informed decisions.
- Increased Research Impact:
- The ability to analyze large datasets more effectively contributed to higher-quality research outcomes, ultimately advancing NIH's mission to improve health and save lives.
More Articles About Business Intelligence Software
5 Inspiring Examples of Data Intelligence - While plastic banner ads and one-size-fits-all messaging were once the order of the day, in our hyper-connected modern age, consumers command far more when it comes to investing in a brand or a business. Niche, product, or industry aside, to connect with your target audience on a personal level, inspire customer loyalty, and accelerate your commercial growth, taking a data-driven approach to your marketing campaigns is vital...
Data Streaming & Demand Paging Problem - The response time of a reporting system needs to be reduced as much as possible even when the reports that the reporting server is producing are very large. The Style Intelligence Solution A report server's response time is measured by recording the time difference between the initial request for a report and when the first page is returned to the end-user. Most other reporting tools retrieve the data needed to create the report, generate the report on the server, and then send either part or all of the finished report back to the requester. This flow can result in very long wait times when a report is larger than a few pages. At best, the wait time would vary linearly with respect to the number of pages in the report...
Evaluate InetSoft's Reporting Tool for Associations - Are you looking for good reporting tools for associations? InetSoft's pioneering BI application produces great-looking dashboards for analyzing membership trends and dues payment performance. View a demo and try interactive examples...
Features to Look for in a Good BI Solution - This section discusses the key features that a business should consider in choosing a BI solution. Data Connectivity: A BI solution's data engine should be able to access any data source, from spreadsheet files to relational databases, data warehouses, big data storages, all the way to on-premise or cloud-based applications that use JSON and REST APIs. The daata engine must be able to handle "big data" applications and be fully scalable to meet changing demands. The solution should multi-tenancy features to allow automated parameterized connection to multiple databases or schemas based on user, group, or role, and should facilitate creation of business-friendly abstraction layers such as entity-attribute models in addition to supporting graphical user-friendly SQL query creation...