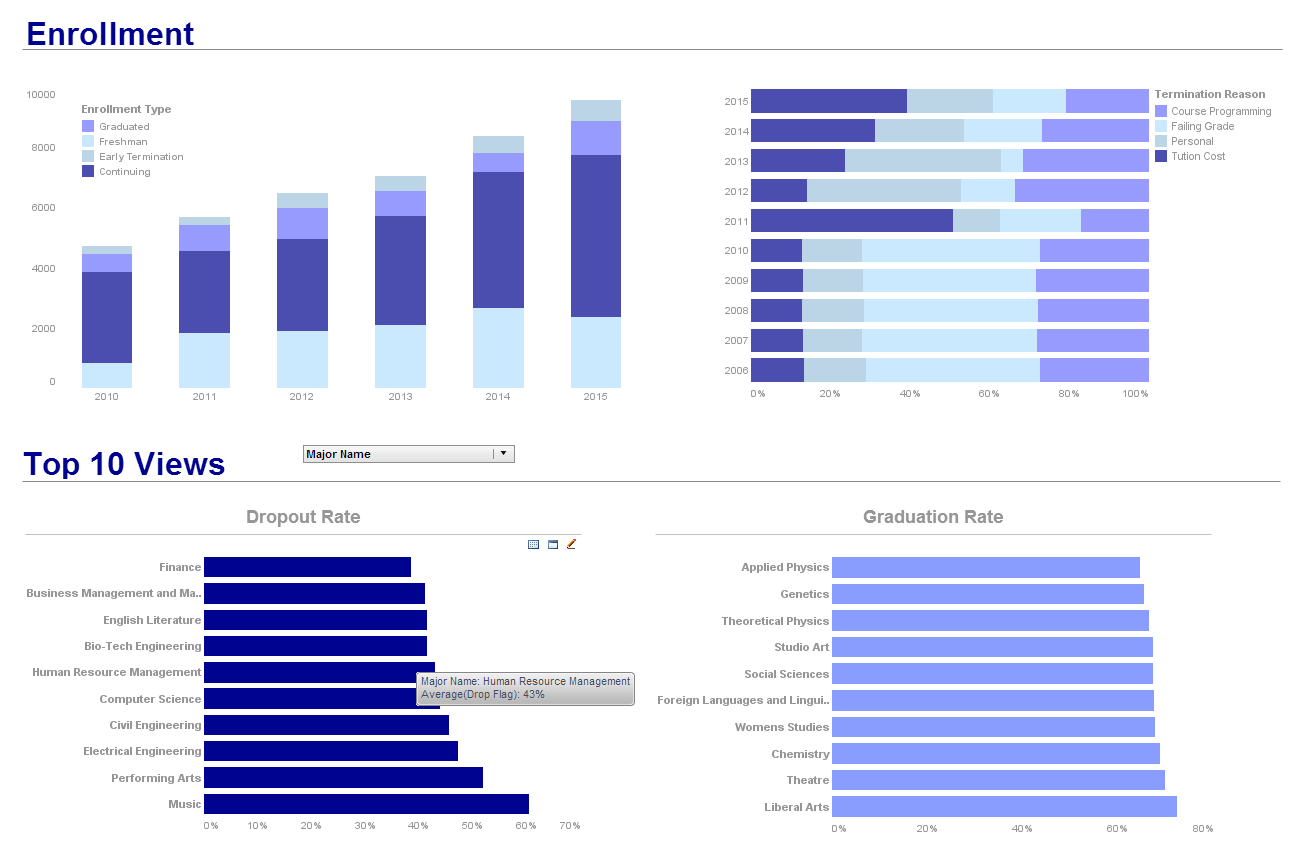
What are the key features successful users of BI need in their data management solutions?
This is a continuation of the transcript of a Webinar hosted by InetSoft entitled "Best Practices for Deploying and Using Business Intelligence Software." The speaker is Mark Flaherty, Vice President of Marketing at InetSoft.
Mark Flaherty (MF): Companies need to be able to accommodate the perpetual trend of growth of their data sets. The average growth of corporate databases each year has been running around 25% per year. In most cases, they need to have a data transformation and cleansing process in place, and they need to be able to optimize queries that their BI applications are making on these large data stores.
What are the data management tools that the best companies are using?
Three-quarters of the best users of business intelligence use system integration tools and data warehouse software, but only about a half use data mining tools.
How do you develop a BI deployment strategy?
The goal is to deploy BI beyond just the BI specialists and database analysts and make it available to any knowledge worker, manager, or executive. Further, you are trying to deliver the information that matters to the key decision makers within the enterprise. Speed of access and timeliness of information are key, as well. Lastly, ease of use has to be a high priority.
In terms of features you want to have in the BI solution, automated report generation and delivery is a must. Some kinds of information are best consumed via KPI dashboards, where people will willingly log in and check out each morning. Other types of information need to be pushed out via email. Otherwise people won’t look at it or act on it.
 |
View a 2-minute demonstration of InetSoft's easy, agile, and robust BI software. |
Another key feature that the best BI deployments have in common is a way to monitor usage levels of the BI system, both the physical resources to ensure satisfactory performance and query times, but also the user adoption levels, so you can identify the champion users and those who need pushing or extra training. Remember the point of deploying a BI solution is to get a higher ROI due to faster, better decision-making and that will tend to increase as more people use they system.
How the Administrator of a BI Platform Can Monitor Its Usage and Performance
Monitoring the usage and performance of a Business Intelligence (BI) platform is critical for administrators to ensure the platform operates efficiently, meets user needs, and delivers accurate insights. Effective monitoring helps in identifying potential issues, optimizing resources, and ensuring compliance with organizational policies. Below is a detailed explanation of how a BI platform administrator can monitor its usage and performance.
1. User Activity Monitoring
User activity monitoring is essential for understanding how the BI platform is being utilized and ensuring that it meets the needs of its users. Administrators can track various aspects of user activity:
-
Login and Access Logs: By monitoring login times, frequency of access, and user roles, administrators can identify patterns in platform usage. For example, if certain users are not logging in regularly, it might indicate a need for additional training or that certain reports are not meeting their needs.
-
Report and Dashboard Access: Administrators can track which reports and dashboards are being accessed most frequently. This helps in understanding which data is most valuable to users and can inform future development efforts. Conversely, reports that are rarely accessed might be candidates for archiving or deprecation.
-
User Actions and Queries: Monitoring the types of queries users run and the actions they take on the platform (e.g., creating new reports, sharing dashboards) provides insights into how users are engaging with the data. This can also help in identifying potential misuse or areas where the system could be optimized to better support user activities.
2. Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring is crucial to ensure that the BI platform is running efficiently and delivering insights in a timely manner. Key aspects of performance monitoring include:
-
System Load and Resource Utilization: Administrators should monitor the CPU, memory, and disk usage of the servers hosting the BI platform. High resource utilization can indicate that the system is under strain and might need scaling or optimization.
-
Query Performance: BI platforms often involve complex queries on large datasets. Monitoring the execution time of these queries is critical. Long-running queries can degrade system performance and frustrate users. Administrators can set thresholds for query performance and receive alerts if these are exceeded.
-
Data Load Times: For platforms that regularly ingest data, the time it takes to load new data into the system is a key performance metric. Slow data loads can delay the availability of fresh insights and impact decision-making. Monitoring these times helps in identifying bottlenecks in the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process.
-
Dashboard Load Times: The time it takes for dashboards to load is directly related to user satisfaction. Slow-loading dashboards can hinder productivity and lead to user dissatisfaction. Monitoring and optimizing dashboard performance is essential for maintaining a positive user experience.
3. Error and Alert Management
Proactive management of errors and alerts is vital for maintaining the reliability of a BI platform. Administrators can monitor:
-
System Errors and Logs: Tracking system errors and application logs helps in identifying recurring issues that might affect the platform's stability. This could include database connection errors, failed report executions, or issues with data refresh processes.
-
User-Reported Issues: Administrators should also keep track of issues reported by users. This could be done through a ticketing system or helpdesk. Monitoring these reports helps in quickly addressing user problems and improving the overall user experience.
-
Automated Alerts: Setting up automated alerts for critical issues such as system downtime, failed data loads, or breaches in security protocols allows administrators to respond quickly to potential problems. Alerts can be configured to notify administrators via email, SMS, or within the platform's monitoring tools.
4. Security Monitoring
Ensuring the security of the BI platform is paramount, particularly when dealing with sensitive or confidential data. Administrators should monitor:
-
User Access Controls: Regularly reviewing and auditing user access rights ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. Monitoring changes to access permissions helps in detecting unauthorized access attempts.
-
Data Encryption and Transfer: Monitoring the encryption status of data both at rest and in transit is essential for protecting data integrity and confidentiality. Any anomalies in data transfer protocols should be flagged and investigated.
-
Compliance Audits: BI platforms often need to comply with various regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Regular monitoring of compliance-related activities, such as data access logs and audit trails, helps ensure that the platform adheres to these regulations.
5. Capacity Planning and Scalability
To ensure the BI platform can handle growing user demands and data volumes, administrators need to monitor and plan for capacity and scalability:
-
Resource Utilization Trends: By analyzing trends in resource utilization (e.g., CPU, memory, storage), administrators can predict when the system might need additional resources or upgrades. This proactive approach helps in avoiding performance bottlenecks.
-
User Growth and Data Volume: Monitoring the growth in the number of users and the volume of data being processed by the platform helps in planning for future capacity needs. As user numbers and data volumes increase, the platform may require scaling (e.g., adding more servers or storage) to maintain performance.
-
Scaling Strategies: Depending on the platform architecture, administrators might employ vertical scaling (adding more power to existing servers) or horizontal scaling (adding more servers) to accommodate growing demands. Monitoring tools can provide insights into which strategy might be more effective.
6. Reporting and Analytics on Platform Usage
Generating reports and analytics on the BI platform's usage and performance provides administrators with actionable insights:
-
Usage Analytics Dashboards: Creating dashboards that track key metrics like active users, report usage, and query performance helps administrators quickly assess the health and usage of the platform.
-
Performance Reports: Regularly scheduled reports on system performance, including server uptime, query response times, and data load times, help in maintaining an optimal environment.
-
Trend Analysis: Analyzing trends over time, such as increases in user activity or changes in resource utilization, can help administrators anticipate future needs and adjust resources accordingly.
7. User Feedback and Training
Monitoring user feedback and providing training are important for improving the overall effectiveness of the BI platform:
-
Feedback Collection: Regularly collecting feedback from users about their experience with the platform can provide valuable insights into areas that need improvement. Surveys, focus groups, or direct feedback channels can be used for this purpose.
-
User Training: Ensuring that users are adequately trained on how to use the BI platform can improve overall usage and satisfaction. Monitoring user activity can help identify individuals or groups who might benefit from additional training.
8. Third-Party Monitoring Tools
In addition to the built-in monitoring capabilities of most BI platforms, administrators can use third-party tools to enhance their monitoring efforts:
-
Application Performance Management (APM) Tools: Tools like New Relic, Dynatrace, or AppDynamics provide deep insights into application performance, including detailed metrics on query performance, user interactions, and system health.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools: SIEM tools such as Splunk or IBM QRadar help in monitoring security-related events and ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
-
Custom Monitoring Solutions: Administrators can also develop custom scripts or dashboards to monitor specific aspects of the BI platform that are not covered by built-in or third-party tools.
| Previous: Best Usage of Business Intelligence |