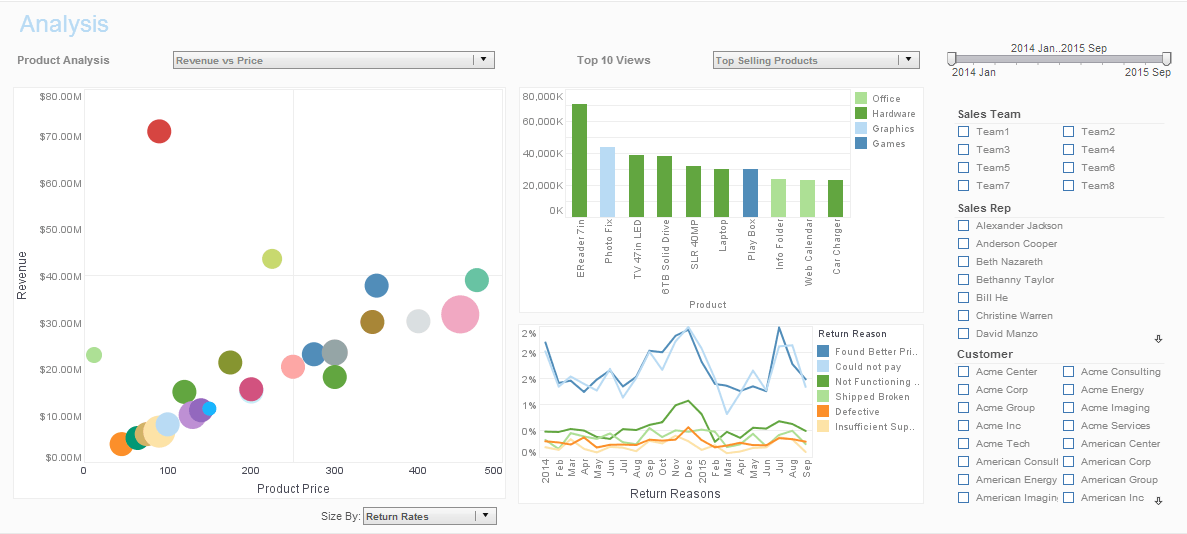
Operational Financial Business Intelligence
Below is the transcript from a podcast from InetSoft Technology. The speaker is Mark Flaherty, CMO at InetSoft.
What does operational business intelligence mean?
Historically people viewed enterprise data warehousing and BI environments as a resting place for data. Now, operational is added to differentiate those types of business intelligence from a real-time environment that is aimed at driving data and analytics and ad hoc data exploration where in the organization that it needs to be, when it needs to be there. That may be in real-time, or really what is better called near-real-time. It may be to data delivered to event-driven systems and systems that require analytics and/or ad hoc queries.
Is the trend towards operational business intelligence accelerating?
It is, especially in financial industries like banking with everything from risk analytics to being able to drive real-time decisioning for credit applications for mortgage or retail loans, for instance. A lot of things banks have done in the past have been driven by lines of business or regulatory compliance issues that they were trying to address. For instance the banking industry you have Basel II, for the insurance industry you have Solvency II. These are regulations that really cause infrastructure changes for the banks and the way they do business, the way they manage data, not only for reports but in the way they look at their business and drive their business.
They can look at these regulations from two perspectives. One is the shrug and the deep sigh. I have to comply with yet another regulation. The other way they can look at it is really the way that the regulations were intended, which is really driving best practice and in Basel’s case, risk management, and in Solvency’s case, risk management for the insurance industry. Take a look at those and be able to drive best practices around those so that they can improve their business and generate better outcomes, versus just complying with the regulatory mandate.
How do you go about bringing value to companies from the tremendous amount of data that they have?
There are two key things. One is our approach. Leveraging provisioning practices that we have come up with, which represents a comprehensive approach to data collection. The second piece of data provisioning is around data management. How to manage the quality, how to manage metrics around that data, how to certify the data for specific uses.
What are the biggest challenges to implementing an enterprise data warehouse and business intelligence environment?
The two main challenges we see are not technology oriented at all. There will always be glitches in the technology that get in the way, but it’s not a limiter at all these days. The real issue is more cultural. Being able to look at data, and the line of business’s desire to have their data the way they want it versus the need for enterprise level data manipulation and being able to manage data at that level. The real challenge becomes one that is cultural. And then figuring out how to measure the value of that data. A program around defining what the enterprise has, what they need, and what the value is, so you can manage data as a corporate asset.
How is artificial intelligence impacting Operational Financial Business Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming Operational Financial Business Intelligence (OFBI) by enabling more sophisticated data analysis, automation of routine tasks, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. This integration of AI with OFBI tools and processes is revolutionizing the way organizations handle financial data and operational performance, making it possible to achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and strategic insight. Below are some of the key ways in which AI is impacting OFBI:
1. Enhanced Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
-
Advanced Analytics: AI enhances traditional data analytics by employing machine learning (ML) algorithms to identify patterns and trends that might be missed by conventional methods. For example, AI can analyze large datasets to detect subtle financial anomalies, such as irregular expense patterns or uncharacteristic revenue fluctuations, providing early warnings of potential issues.
-
Predictive Modeling: AI enables predictive analytics in OFBI, allowing businesses to forecast financial outcomes with higher accuracy. This can include predicting cash flow trends, sales performance, and even potential financial risks. For example, machine learning models can predict future revenue based on historical data, seasonal trends, and external market factors, helping businesses to plan more effectively.
-
Scenario Analysis: AI facilitates complex scenario modeling, where businesses can simulate various operational and financial scenarios to see potential outcomes. This is particularly useful for risk management, as it allows companies to assess the impact of different decisions, such as changes in pricing strategy, cost reductions, or investment in new markets.
2. Automation of Financial Processes
-
Automated Reporting: AI automates the generation of financial reports, reducing the time and effort required to compile data and minimizing human error. Natural Language Processing (NLP) can be used to generate narrative explanations for financial results, making reports more accessible to non-financial stakeholders.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA, powered by AI, automates repetitive financial tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and reconciliation. This not only speeds up these processes but also frees up human resources for more strategic activities, such as financial planning and analysis.
-
Intelligent Financial Planning: AI-driven tools can automate budget creation and monitoring, adjusting financial plans based on real-time data. This dynamic approach to financial planning ensures that organizations remain agile and can quickly adapt to changes in their financial environment.
3. Real-Time Operational Insights
-
Dynamic Dashboards: AI enhances OFBI dashboards by integrating real-time data feeds, enabling organizations to monitor financial and operational metrics as they change. For example, AI can track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as operating margins, cash flow, and inventory levels, providing instant insights that can inform decision-making.
-
Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms are highly effective at identifying anomalies in financial data, such as unexpected spikes in expenses or unusual transactions. These anomalies can be flagged for review, helping businesses to quickly address potential issues such as fraud or inefficiencies in operational processes.
-
Operational Efficiency Optimization: AI can analyze operational data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in business processes. For example, by analyzing supply chain data, AI can suggest optimizations that reduce costs and improve delivery times, which in turn impacts financial performance.
4. Improved Financial Forecasting and Budgeting
-
Enhanced Forecast Accuracy: AI-driven forecasting models use vast amounts of historical and real-time data to improve the accuracy of financial forecasts. These models can factor in a wide range of variables, such as market trends, customer behavior, and macroeconomic indicators, to provide more reliable forecasts than traditional methods.
-
Adaptive Budgeting: AI enables continuous and adaptive budgeting processes, allowing businesses to adjust their budgets in response to changing circumstances. This is particularly useful in volatile markets, where static annual budgets may quickly become outdated.
-
Revenue Optimization: AI can analyze sales data, customer preferences, and market conditions to identify opportunities for revenue growth. For instance, AI models can predict which products are likely to be in demand and suggest optimal pricing strategies.
5. Improved Risk Management
-
Credit Risk Assessment: AI models can assess credit risk more accurately by analyzing a broad range of data points, including financial statements, payment history, and even social media activity. This allows financial institutions to make more informed lending decisions and reduce the risk of defaults.
-
Fraud Detection and Prevention: AI excels at detecting patterns associated with fraudulent activity. By analyzing transactional data in real time, AI systems can flag suspicious activities for further investigation, reducing the risk of financial losses due to fraud.
-
Operational Risk Management: AI can identify and quantify operational risks, such as supply chain disruptions or regulatory compliance issues, enabling businesses to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks.
6. Enhanced Decision-Making Support
-
Decision Support Systems: AI-powered decision support systems provide executives with data-driven insights and recommendations. These systems can analyze complex datasets and simulate the outcomes of various business decisions, supporting more informed strategic planning.
-
Sentiment Analysis: AI can analyze unstructured data, such as news articles, social media posts, and customer reviews, to gauge market sentiment and its potential impact on financial performance. This can help businesses anticipate changes in consumer behavior or investor sentiment.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables the extraction of insights from textual data, such as earnings call transcripts, financial reports, and news articles. This helps financial analysts to quickly identify key information and trends that could impact business performance.
7. Personalization of Financial Services
-
Customized Financial Reporting: AI can tailor financial reports and dashboards to the specific needs of different stakeholders, providing relevant information without overwhelming them with unnecessary details. For instance, executives might receive high-level summaries, while finance teams get access to detailed data and analytics.
-
Personalized Recommendations: AI can provide personalized financial advice based on individual or organizational financial health, goals, and market conditions. This can be particularly useful in wealth management and investment advisory services.
-
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can answer questions about financial data, generate reports, and even perform basic analysis. This improves accessibility to financial insights for non-expert users.