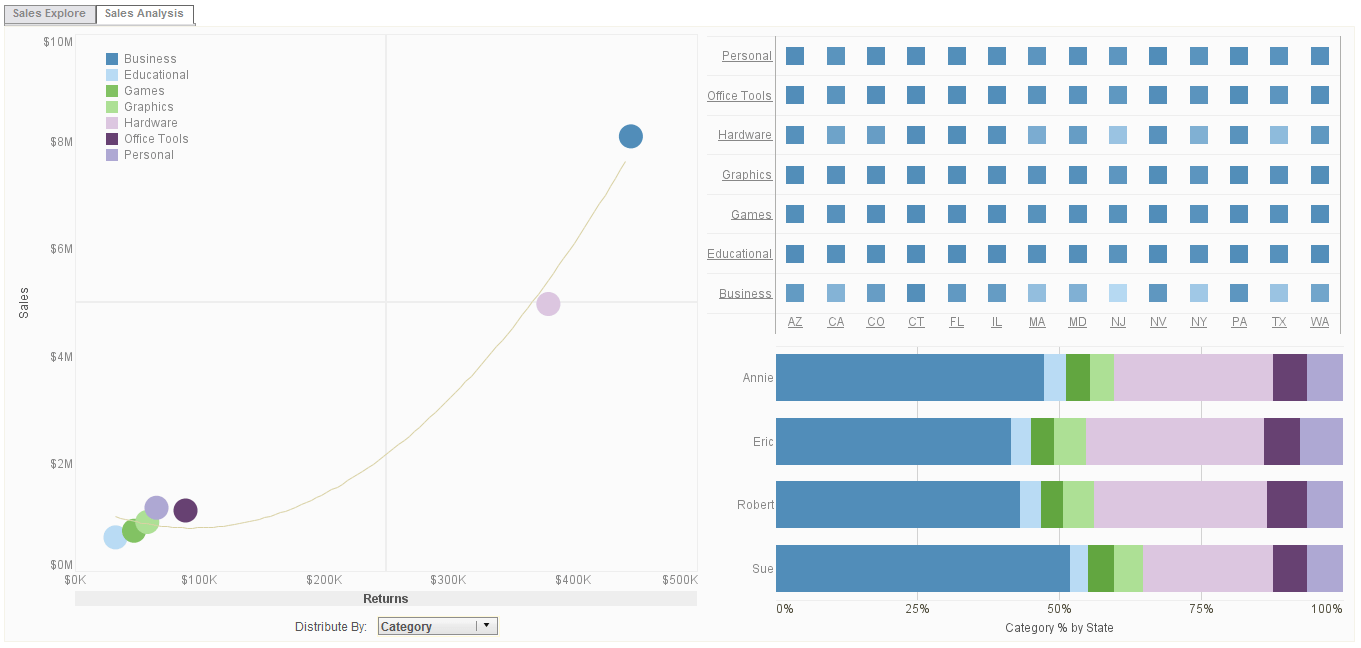
Great Success in Facilitating Data Exploration
This is the continuation of the transcript of a Webinar hosted by InetSoft on the topic of "10 Biggest Big Data Trends."
Where we have seen great success with InetSoft is in facilitating data exploration. We talked about the rising self-service data prep tools. That has helped people be able to blend data for multiple sources where in the past they would've had to go through ETL work to the data warehouse, they are able to do that more on-the-fly, more agilely.
So all of these technologies have grown because ultimately end users, business users have not been able to have their needs met in the waterfall model, and what we have seen with our customers and with those central BI teams, again be it in IT or in the business, they are facilitating a relationship where they are iterating and working together.
Certified Data Sources
Through a central model you have certified data sources and great visibility into what people are doing and lineage and impact analysis on changes in worksheets and things like that. But ultimately the people in the business are empowered to ask questions and answer the question. So that certainly is what we see and we expect Big Data just facilitates this even more because it's more types of data to answer all other types of questions. Holly and Larry, anything to add?
Holly: Yes. I would like to comment actually on the waterfall question a little bit or from a different perspective. So if your approach to BI is only that waterfall approach, I think you'll be dead in the water. You just can't react fast enough. And the analogy that I would like to use to sort of illustrate that is the pop-up store. You probably have seen an increasing popular concept in the retail space of pop-up stores where you get a retail space appearing for a short time for a specific purpose perhaps in a location and we are seeing a lots more of those pop-up stores.
And I think of the new BI as being more like the ability to support pop-up BI, pop-up data warehouses, pop-up insight at the time of need. It's agility, and that's where the comparison to waterfall is where InetSoft is coming from. Some other questions are around, do you recommend this particular technology or vendor either in the cloud or Big Data or data access, and they are usually quite agnostic about this. So I usually counsel our customers to ask this one question when they're evaluating a platform or tool, and that is, will it keep us agile? Will I be able to do pop-up analysis with this tool, with this strategy, with this platform?
Abhishek: That's a key, and we are going to come to the question specifically on is there a recommended Cloud data warehouse and preferred vendor for InetSoft. For us to get back to again enabling our customers to be agile, working with the data source is important to them. So it's a little bit of, have faith in us and trust in us that we will try to be as agnostic as possible and work with the leading data sources and give us the feedback on what important ones are.
But I think of the cloud data warehouses where InetSoft has direct connectivity and has worked really hard to optimize our connections with, Amazon Redshift, and Snowflake and SQL data warehouse, Google Big Query and Teradata Cloud which are not the only Cloud data warehouses but essentially the leading ones.
And then in addition to those are MPPs, purpose built data warehouses. You have your traditional relational databases that are still being used for analytics or data warehousing use cases like Amazon, Aurora, and SQL Database, and Google Cloud SQL. And so InetSoft's mission and vision is to work with as many data sources as possible and be very source agnostic.
So we don't have a preferred vendor. We have several preferred ones that we work closely with and definitely encourage customers to find the right use case and the right product for it.
Case Study: Enhancing Operations and Decision-Making in Shopping Center Management Through Data Exploration Tools
Global Malls Inc. is a mid-sized company managing a portfolio of 15 shopping centers across North America. These centers serve a diverse range of customers, offering retail stores, dining options, entertainment, and event spaces. Each center operates independently, but the corporate office oversees general management, leasing, and tenant relations. The business model is driven by maximizing tenant occupancy, optimizing foot traffic, and providing an excellent customer experience to attract shoppers and boost sales for tenants.
The competitive landscape of the retail sector has become increasingly challenging, with e-commerce rising and shifting consumer preferences. Shopping centers have been compelled to reinvent themselves by focusing on customer engagement, experience, and operational efficiency. Global Malls realized that making decisions purely based on historical data and intuition was no longer effective. They needed better insights into tenant performance, foot traffic, customer preferences, and center operations. This prompted the adoption of data exploration tools to improve operations, decision-making, and overall performance.
Challenge: Operational Inefficiency and Lack of Actionable Insights
Before embracing data exploration tools, Global Malls faced several critical challenges:
-
Fragmented Data: Each shopping center operated independently, collecting different kinds of data. Some collected foot traffic, others gathered sales information from tenants, while a few focused on marketing and customer satisfaction surveys. However, the data was stored in silos, making it hard to extract actionable insights at the corporate level.
-
Uninformed Leasing Decisions: The leasing team lacked the data needed to predict which tenants would be the best fit for the available spaces. Without detailed information on customer preferences or emerging market trends, decisions were often reactive, based on past performance or general industry trends.
-
Inefficient Marketing Campaigns: Marketing campaigns were often run without any feedback loop or clear metrics to determine their success. This led to wasted marketing spend and missed opportunities to target key customer demographics.
-
Lack of Customer Understanding: There was limited understanding of the behaviors, demographics, and preferences of shoppers visiting the malls. This gap made it difficult to optimize tenant mix, events, and experiences tailored to local audiences.
-
Limited Insights Into Foot Traffic: Data on foot traffic was either outdated or incomplete. Global Malls struggled to analyze trends or predict peak shopping periods, leading to suboptimal staffing and operations.
To address these problems, the company knew it had to move beyond traditional methods of analyzing data and embrace a more dynamic and exploratory approach.
Solution: Implementing Data Exploration Tools
Global Malls decided to invest in data exploration and business intelligence (BI) tools to consolidate, analyze, and visualize data across its shopping centers. After careful evaluation, the company selected a suite of tools designed for data integration, visualization, and real-time analytics. Some of the key tools adopted included:
-
InetSoft Data Mashup Tool: This allowed Global Malls to combine data from different sources—tenant sales, foot traffic counters, CRM systems, and social media engagement—into a single platform. By mashing up these data sets, they gained comprehensive insights into how different factors interacted and influenced business outcomes.
-
Tableau for Data Visualization: Tableau's visual analytics platform enabled Global Malls' team to create dashboards that provided a clear and intuitive understanding of foot traffic patterns, tenant performance, and customer preferences across various dimensions (time of day, weekends vs. weekdays, holiday periods, etc.).
-
Google Analytics & Heat Mapping Software: For deeper insights into customer behavior, the company used Google Analytics to track the effectiveness of digital marketing campaigns and heat mapping tools to analyze shopper movements within the malls. Heat maps helped visualize high-traffic areas and areas of low engagement.
-
Predictive Analytics Tools: They also integrated AI-powered predictive analytics software to forecast trends in foot traffic, tenant success, and potential tenant mix optimization.
Implementation Process
Global Malls took a phased approach to implementing the data exploration tools across its shopping centers:
-
Data Consolidation: The first step involved gathering all available data from different centers and integrating them using the InetSoft data mashup tool. By combining tenant sales reports, foot traffic data from IoT sensors, marketing data from social media, and customer feedback surveys, Global Malls achieved a unified view of their operational metrics.
-
Dashboard Development: The next step was creating dashboards using Tableau. These dashboards allowed mall managers to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as daily foot traffic, tenant sales per square foot, and customer satisfaction scores. Executives could access high-level, aggregated data across all centers, while local managers could drill down into data specific to their mall.
-
Training: Employees at both corporate and individual mall locations were trained on how to use the data exploration tools. Training focused on identifying valuable insights, creating custom reports, and setting up automated alerts for outlier trends or issues (e.g., sudden drops in foot traffic).
-
AI-Powered Predictions: With predictive analytics, Global Malls started forecasting future trends, such as the impact of events on foot traffic or predicting when certain tenants might be at risk of underperformance. These forecasts were incorporated into decision-making processes for leasing, marketing, and operations.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Iteration: After the initial implementation, the tools were continuously monitored and iterated upon. As more data became available, the dashboards were updated, and new reports were generated to refine the company's understanding of customer behavior and business performance.
Results: Data-Driven Transformation
The implementation of data exploration tools brought significant improvements across multiple facets of Global Malls' business operations:
-
Optimized Tenant Mix: With access to data on customer demographics and shopping preferences, the leasing team made more informed decisions about tenant placement. They began choosing tenants based on data-driven forecasts of how well each tenant's target market aligned with local foot traffic patterns and customer preferences. This resulted in higher tenant retention and satisfaction rates, as the right businesses were placed in the right malls.
-
Improved Marketing Campaign Effectiveness: Marketing campaigns became more targeted and data-driven. By analyzing customer data collected from foot traffic sensors, online surveys, and social media, the marketing team developed campaigns that spoke directly to the needs and desires of local shoppers. Heat mapping helped identify popular areas within malls where digital signage and pop-up events could generate the highest engagement. Campaigns were also analyzed in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments to improve ROI.
-
Enhanced Foot Traffic Insights: Dashboards provided real-time data on foot traffic, allowing mall managers to anticipate busy periods and optimize staffing accordingly. For example, during the holiday season, foot traffic data helped plan for increased security, janitorial services, and even promotions during peak hours. This proactive approach improved the overall shopping experience, reducing wait times and congestion in key areas.
-
Efficient Space Utilization: Heat mapping revealed underutilized spaces within the shopping centers. This insight allowed mall managers to reposition certain stores, add seating areas, or incorporate kiosks in high-traffic zones. Optimizing space utilization not only increased shopper satisfaction but also led to new revenue streams from previously underperforming areas.
-
Actionable Customer Insights: Data collected from social media and CRM tools provided a deeper understanding of customer preferences. Global Malls introduced customer loyalty programs based on these insights, offering personalized discounts and promotions. This fostered stronger relationships with shoppers, driving repeat visits and increasing the time and money spent per customer.
-
Predictive Maintenance and Cost Savings: Predictive analytics tools allowed Global Malls to anticipate maintenance needs. By analyzing patterns in equipment use, the system could predict when elevators, escalators, or HVAC systems were likely to fail, enabling preemptive repairs. This reduced maintenance costs and minimized downtime for mall operations.