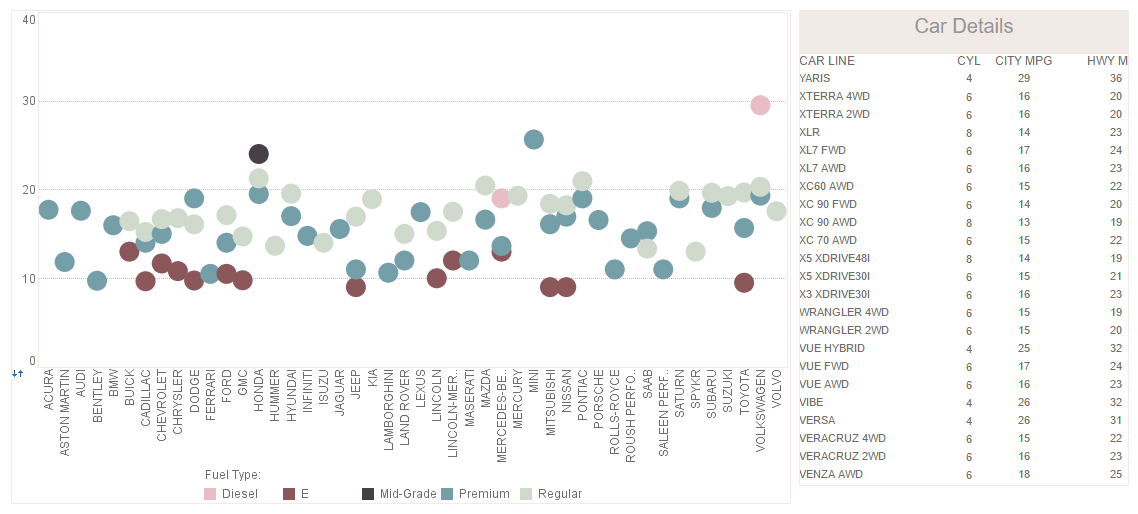
How to Make a Bubble Chart Using the API
Are you looking for a way to create bubble charts? InetSoft offers both free and commercial software for making bubble charts.Visualize Free is a free visual analysis application. No software to install, just upload your spreadsheet. In a few minutes you have dynamically interactive bubble charts to explore your data.
Below developers can learn how to use InetSoft's API to create a bubble chart.
SizeFrame.setLargest(value) / SizeFrame.Largest
Specifies the highest value in the range. For point and line graphs, this is the size (in pixels) at which the largest value in the bound column is displayed. Smaller values are scaled according to the mapping defined by the object's scaling method (e.g., linear for LinearSizeFrame, etc.).
For schema and bar graphs, the value specified for the largest property is relative to the SizeFrame.setMax(value) / SizeFrame.max value. For example, if largest=50 and max=100, the largest value in the bound column is displayed at one half of the maximum allowable size. The value of largest should be less than the value of max.
Parameter/Type
value Number of pixels, or relative size
Example (Report)
Bind a point-type chart to the sample 'All Sales' query, with 'Company' (top 5) on the X-axis, and Sum(Total) on the Y-axis. Add the following script in the onLoad Handler.
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic);
Graph1.bindingInfo.setSizeField("Total",Chart.NUMBER);
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame = new LinearSizeFrame;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.smallest = 10;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.largest = 50;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.max = 100;
Example (Report or Viewsheet)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.element)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.scale)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.data)
var arr = [["State", "Quantity", "width"], ["NJ", 200, 5], ["NY", 300,10], ["PA",75,15]];
dataset = new DefaultDataSet(arr);
graph = new EGraph();
var elem = new IntervalElement("State", "Quantity")
elem.sizeFrame = new LinearSizeFrame();
elem.sizeFrame.setField("width");
elem.sizeFrame.setSmallest(10);
elem.sizeFrame.setLargest(50);
elem.sizeFrame.setMax(100);
graph.addElement(elem);
SizeFrame.setMax(value) / SizeFrame.max
Specifies an arbitrary value representing the maximum allowable size for a graphical element. For schema and bar graphs, the values specified for the SizeFrame.setLargest(value) / SizeFrame.Largest and SizeFrame.setSmallest(value) / SizeFrame.smallest properties are relative to the max value. For example, if smallest=50 and max=100, the smallest value in the bound column is displayed at one half of the maximum allowable size. For point and line graphs, the max property is ignored.
Parameter/Type
value Number of pixels, or relative size
Example (Report)
Bind a point-type chart to the sample 'All Sales' query, with 'Company' (top 5) on the X-axis, and Sum(Total) on the Y-axis. Add the following script in the onLoad Handler.
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic);
Graph1.bindingInfo.setSizeField("Total",Chart.NUMBER);
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame = new LinearSizeFrame;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.smallest = 10;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.largest = 50;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.max = 100;
Example (Report or Viewsheet)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.element)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.scale)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.data)
var arr = [["State", "Quantity", "width"], ["NJ", 200, 5],
["NY", 300,10], ["PA",75,15]];
dataset = new DefaultDataSet(arr);
graph = new EGraph();
var elem = new IntervalElement("State", "Quantity")
elem.sizeFrame = new LinearSizeFrame();
elem.sizeFrame.setField("width");
elem.sizeFrame.setSmallest(10);
elem.sizeFrame.setLargest(50);
elem.sizeFrame.setMax(100);
graph.addElement(elem);
SizeFrame.setSmallest(value) / SizeFrame.smallest
Specifies the lowest value in the range. For point and line graphs, this is the size (in pixels) at which the smallest value in the bound column is displayed. Larger values are scaled according to the mapping defined by the object's scaling method (e.g., linear for LinearSizeFrame, etc.).
For schema and bar graphs, the value specified for the smallest property is relative to the SizeFrame.setMax(value) / SizeFrame.max value. For example, if smallest=50 and max=100, the smallest value in the bound column is displayed at one half of the maximum allowable size.
Parameter/Type
value Number of pixels, or relative size
Example (Report)
Bind a point-type chart to the sample 'All Sales' query, with 'Company' (top 5) on the X-axis, and Sum(Total) on the Y-axis. Add the following script in the onLoad Handler.
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic);
Graph1.bindingInfo.setSizeField("Total",Chart.NUMBER);
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame = new LinearSizeFrame;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.smallest = 10;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.largest = 50;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.max = 100;
Example (Report or Viewsheet)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.element)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.scale)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.data)
var arr = [["State", "Quantity", "width"], ["NJ", 200, 5], ["NY", 300,10], ["PA",75,15]];
dataset = new DefaultDataSet(arr);
graph = new EGraph();
var elem = new IntervalElement("State", "Quantity")
elem.sizeFrame = new LinearSizeFrame();
elem.sizeFrame.setField("width");
elem.sizeFrame.setSmallest(10);
elem.sizeFrame.setLargest(50);
elem.sizeFrame.setMax(100);
graph.addElement(elem);
StaticSizeFrame
The StaticSizeFrame object contains a size frame defined by explicit size data in the VisualFrame.setField(field) column, or by the fixed size in StaticSizeFrame.setSize(value) / StaticSizeFrame.size. To create a StaticSizeFrame object, call the StaticSizeFrame constructor.
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic); var frame = new StaticSizeFrame(10);
You can pass a numerical size (e.g., 10) to the constructor, or specify this later using the StaticSizeFrame.setSize(value) / StaticSizeFrame.size property.
Example (Report)
Bind a point-type chart to the sample 'All Sales' query, with 'Company' (top 5) on the X-axis, and Sum(Total) on the Y-axis. Add the following script in the onLoad Handler.
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic);
Graph1.bindingInfo.setSizeField("Company",Chart.STRING);
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame = new StaticSizeFrame;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.setSize(30);
Example (Report or Viewsheet)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.element)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.scale)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.data)
var arr = [["State","Quantity","Size"],
["NJ",200,1], ["NY",300,10]];
dataset = new DefaultDataSet(arr);
graph = new EGraph();
var elem = new IntervalElement("State", "Quantity");
var frame = new StaticSizeFrame();
frame.setField("Size");
elem.setSizeFrame(frame);
graph.addElement(elem);
StaticSizeFrame.setSize(value) / StaticSizeFrame.size
Specifies the static size for graphical elements. For point and line graphs, this is the size (in pixels) of the elements. For schema and bar graphs, the value specified for the size property is relative to the SizeFrame.setMax(value) / SizeFrame.max value (default = 30). For example, if size=50 and max=100, the graphical elements are displayed at one half of the maximum allowable size.
If the data in the column assigned to the inherited VisualFrame.setField(field) property are positive values, these data values are used instead of StaticSizeFrame.size.
Parameter/Type
value Number of pixels, or relative size
Example (Report)
Bind a point-type chart to the sample 'All Sales' query, with 'Company' (top 5) on the X-axis, and Sum(Total) on the Y-axis. Add the following script in the onLoad Handler.
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic);
Graph1.bindingInfo.setSizeField("Company",Chart.STRING);
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame = new StaticSizeFrame;
Graph1.bindingInfo.sizeFrame.size = 30;
Example (Report or Viewsheet)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.element)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.scale)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.aesthetic)
importPackage(inetsoft.graph.data)
var arr = [["State","Quantity"], ["NJ",200], ["NY",300]];
dataset = new DefaultDataSet(arr);
graph = new EGraph();
var elem = new IntervalElement("State", "Quantity")
var frame = new StaticSizeFrame();
frame.setMax(100);
frame.setSize(50);
elem.setSizeFrame(frame);
graph.addElement(elem);