The Drive Towards Self-Service Reporting
The reasons for heading towards self-service reporting are almost self-evident. There are constant budget pressures, yet competitive pressures call for increased access to relevant information. IT can be caught in the middle. The pragmatic decision is to shed some of the centralized reporting function housed in IT and enable self-service reporting by business users.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
The Historical and Technological Trends
Years ago, this might have sounded like a radical new way of delivering information, but the trend was set in place with the advent of reporting tools as rudimentary as Crystal Reports. In the 1990s, it was the de facto standard for desktop-based reporting. While sophisticated report writing still requires specialized skills and database knowledge, now even more sophisticated interactive reporting software, such as InetSoft’s, make it even more realistic to enable more self-service reporting.
Now these reporting tools have become more intuitive and easy to work with. Business users, most of the time power users, can build their own reports with relative ease. Not-so-technical users can both customize the reports given to them by the power users and, when provided well-designed interactive reporting interfaces, drill through many reports that previously would have had to have been built individually.IT’s Continued Role in a Self-Service Reporting Deployment
IT responsibilities do not disappear, of course, for self-service reporting. Rather they are focused on tool selection, setup, administration, on delivering quality data on time, and production reporting. Data model setup is probably the most important step where databases are identified and mapped, and complex field names are given easy to understand labels, and users are given dictionaries of field explanations.
Another benefit IT enjoys: the reduction in headaches and lost time due to poorly thought-out business requirements for reports. Even if complex reports need IT development, business users can now prototype them to a greater extent, and certainly understand their data better with greater hands-on experience to speed up iterations.Key Considerations for Successful Reporting Projects
If there are caveats to self-service reporting, they would include the potential dilution of knowledge resulting from spreading the reporting function across various lines of business, something that is exacerbated by the anthropological tendency for departmental silo-ing. Ironically, that undesirable outcome reminds one of the old days when information and database silos cropped across the enterprise, which itself spawned the business intelligence solutions of today.
And do not forget the value of the single version of the truth. The IT department still has a role to play in publishing common definitions and educating users how to find data, or in other cases constructing the approved virtual data models that work off of the centralized data warehouse. There is a risk that a user might calculate a metric in a way that is different from the corporate standardized definition.
Along these lines, a good self-service reporting solution should be routinely monitored by IT. In larger organizations this might mean creating an organization structure to support these changes.
Case Study: Tactical Gear Manufacturer Enhances Decision-Making with Self-Service Reporting
Bravo Defense Solutions (BDS), a mid-sized tactical gear manufacturer, specializes in producing equipment for military, law enforcement, and outdoor enthusiasts. Their product line includes body armor, tactical backpacks, and modular attachment systems. Operating in a competitive market, BDS faced growing pressure to optimize operations, improve product quality, and respond quickly to shifting customer demands. The company's leadership recognized that data-driven decision-making was essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Challenges:
Before adopting self-service reporting, BDS faced several challenges:
-
Siloed Data Systems: Key business data was scattered across multiple systems—ERP for production, CRM for sales, and a separate inventory management tool. This fragmentation hindered a holistic view of operations.
-
Dependence on IT: Generating reports required IT intervention, creating bottlenecks. This delayed access to critical insights, especially for non-technical teams like sales and production.
-
Limited Insights: Static, pre-defined reports didn't allow teams to explore data dynamically or ask follow-up questions. This rigidity limited the depth of analysis.
Solution Implementation:
BDS implemented InetSoft's business intelligence platform that offered robust self-service reporting capabilities. The implementation process included:
-
Data Integration: Leveraging the platform's data mashup tools, BDS unified data from their ERP, CRM, and inventory systems into a centralized repository.
-
Training Programs: Comprehensive training sessions were conducted for staff, focusing on building customized dashboards and running ad-hoc analyses.
-
Customizable Dashboards: The platform allowed users to create role-specific dashboards. For instance, production managers could track output and defect rates, while the sales team monitored regional performance.
Results:
The adoption of self-service reporting transformed BDS's operations in several key areas:
-
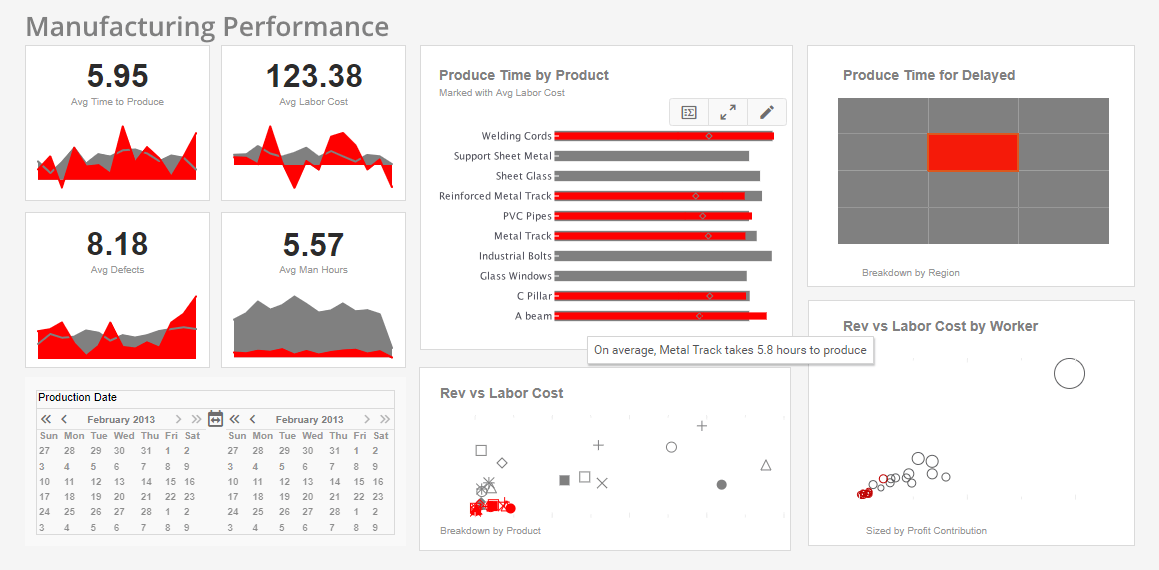
Improved Operational Efficiency: Production managers utilized real-time dashboards to monitor manufacturing performance. When defect rates in a new line of body armor exceeded benchmarks, managers quickly identified and resolved the issue by adjusting machinery settings.
-
Faster Decision-Making: Sales teams no longer waited days for IT-generated reports. They used self-service tools to analyze customer purchasing patterns, enabling faster responses to market trends, such as increasing demand for lightweight tactical gear.
-
Enhanced Inventory Management: The inventory team tracked stock levels and lead times with greater precision. When a surge in demand for tactical backpacks occurred, they quickly adjusted procurement schedules to prevent stockouts.
-
Cost Savings: BDS saved on IT resources by reducing the need for custom report generation. Non-technical staff's ability to generate insights independently freed IT to focus on strategic projects.
Key Takeaways:
-
Empowerment Through Data: Self-service reporting enabled BDS employees to take ownership of their data, fostering a culture of accountability and proactive problem-solving.
-
Agility in a Competitive Market: By providing teams with real-time insights, BDS adapted swiftly to market shifts, reinforcing its position as a leader in tactical gear manufacturing.
-
Scalability for Future Growth: The platform's scalability ensured that BDS could continue leveraging data insights as the company expanded operations and introduced new