What KPIs and Analytics Does a Product Support Analyst Use?
Businesses depend on data-driven insights for product development and customer centricity to make wise choices. The Product Support Analyst (PSA) is one of the important participants in this process.
These experts are in charge of making sure that goods live up to client expectations and fixing any potential problems. PSAs use a variety of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and analytics to accomplish these objectives.
The following article will discuss the KPIs and analytics a Product Support Analyst uses to improve product performance, customer happiness, and company success.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Defining the Role of a Product Support Analyst
The function of a Product Support Analyst must be understood before diving into the KPIs and analytics. PSAs are essential to the stage of a product's life cycle after launch. They serve as a link between stakeholders, product development teams, and consumers. Their main duties are as follows:
- Customer Issue Resolution: To guarantee a great customer experience, problems with customers must be quickly identified, troubleshooted, and resolved.
- Product Performance Monitoring: Analyzing product performance data to spot problem areas and enhance the user experience as a whole.
- Customer Feedback Analysis: obtaining and examining client input to identify problems, tastes, and expectations.
- Product Improvement: collaborating with the product development team to put user feedback and ideas into practice.
Essential KPIs for a Product Support Analyst
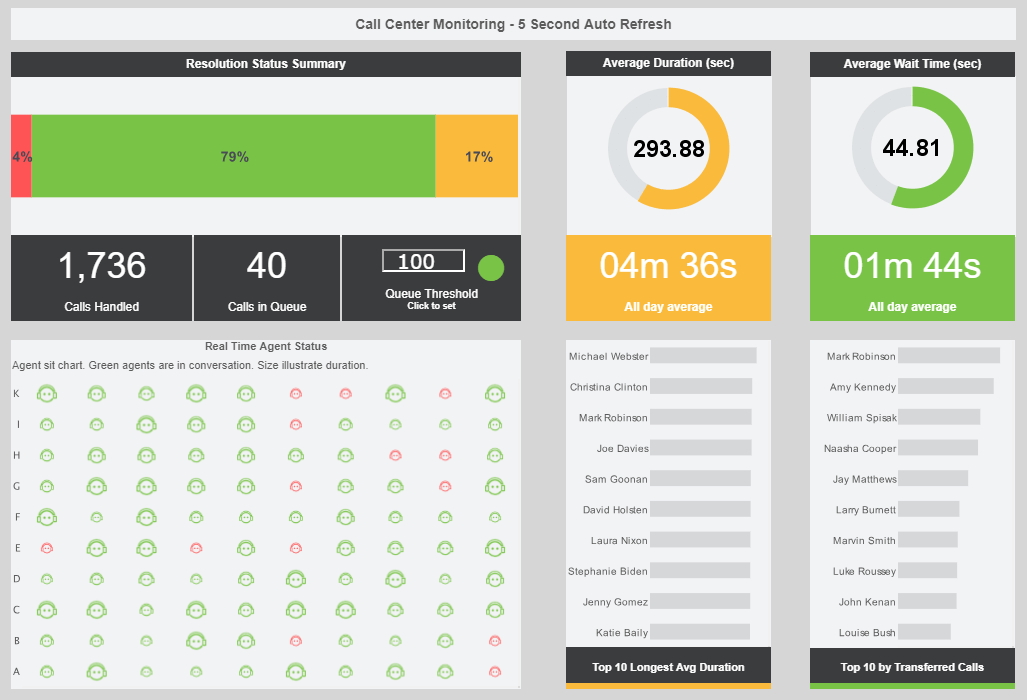
First Response Time (FRT)
FRT tracks how quickly a PSA responds to a customer question or concern once it has been raised. A low FRT is crucial since it shows that the assistance procedure is quick and effective. Customers like prompt replies, and a lower FRT may increase client retention and satisfaction.
Time to Resolution (TTR)
TTR gauges how long it takes a PSA to address a consumer concern once it is raised. A brief TTR suggests effective problem-solving skills, which may raise customer satisfaction and lower turnover.
Ticket Volume and Backlog
Important KPIs to track workload and resource allocation include the quantity of support tickets received and the backlog of unsolved problems. A large number of tickets or a backlog may be a sign that the usability of the product or customer training needs to be improved.
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
CSAT is a popular statistic that assesses how satisfied customers are with the help they get. After fixing a problem, PSAs collect consumer input and determine the CSAT score. This KPI helps pinpoint areas for improvement and offers insightful information about how well support initiatives are working.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Customers are asked to assess their likelihood to suggest a product or service to others on a scale of 0 to 10, which is used by NPS to measure customer loyalty and advocacy. PSAs employ NPS input to determine the general level of consumer satisfaction and to pinpoint prospective brand supporters or detractors.
Churn Rate
The proportion of customers that discontinue utilizing the product or service over a certain time period is measured by the churn rate. PSAs monitor turnover rates to better understand customer attrition and strive to lower it by resolving issues and improving the offering.
Analytics Tools Used by Product Support Analysts
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
In order to organize and track customer contacts, support requests, and response timeframes, CRMs are essential to the workflow of PSAs. These solutions provide PSAs a thorough understanding of client data, enabling them to deliver individualized help.
Product Analytics Tools
PSAs may monitor the effects of modifications or updates and find areas for improvement with the use of product analytics tools. PSAs may use these tools to make data-driven choices that will improve the performance of their products.
Text Analytics
Text analytics software examines unstructured data from sources including support tickets, social media comments, and consumer feedback. These techniques are used by PSAs to glean insightful information from massive volumes of textual data, improving problem recognition and resolution.
User Behavior Tracking
PSAs employ methods for monitoring user activity to learn how consumers use the product. These insights aid in identifying user behavior trends, areas of misunderstanding, and possible barriers.
Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization software transforms complicated data sets into understandable graphics like graphs and charts. These graphics help PSAs communicate their results to stakeholders clearly and spot trends or patterns in the supporting data.
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
Additional KPIs for a Product Support Analyst
Customer Retention Rate
The proportion of consumers that continue to use the product or service over a certain time period is known as the customer retention rate. PSAs track this KPI to see if customer engagement and loyalty are being maintained as a result of support initiatives.
Escalation Rate
The Escalation Rate measures how often support problems must be escalated to management or higher-level support teams. The need for more specialist assistance or gaps in product documentation may be indicated by a high escalation rate.
Self-Service Adoption Rate
This KPI calculates the proportion of users that utilize self-service tools like chatbots, knowledge bases, and FAQs to resolve their problems without calling support. The effort of the support crew may be decreased and the overall customer experience can be improved with higher self-service adoption rates.
Resolution Rate by Tier
Tracking the Resolution Rate by Tier offers insights into the effectiveness of each tier when support staff are divided into tiers based on competence. It aids in identifying areas that could benefit from extra training or assistance.
Time to Escalation
The time it takes to escalate a customer problem to a higher service level or management is measured as "Time to Escalation." In order to provide quick answers to difficult situations, PSAs try to make this time as brief as feasible.
Customer Effort Score (CES)
CES assesses how simple it is for customers to get help. The amount of effort consumers had to expend to resolve their problems is gathered via PSAs. A low CES suggests an efficient support system, which improves customer satisfaction.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Advanced Analytics Tools Used by Product Support Analysts
Sentiment Analysis
In order to ascertain the sentiment or emotional tone underlying their communications, sentiment analysis systems analyze client interactions and comments. This study is used by PSAs to determine consumer happiness and identify prospective problems that may not be clearly expressed.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis entails looking into the fundamental causes of persistent customer problems. PSAs utilize this analytical method to pinpoint the main issues and collaborate with product development teams to put lasting fixes into place.
Cohort Analysis
Customer groups are created using cohort analysis based on details like the date of purchase or the product version. This method is used by PSAs to spot patterns and comprehend how various client demographics engage with the product over time.
Customer Segmentation
By dividing the client base into different groups according to certain characteristics or behaviors, customer segmentation. PSAs use this method to customize support techniques for various segments, ensuring that each group receives specialized help.
Predictive Analytics
In order to forecast future occurrences, such as consumer behavior or possible problems, predictive analytics utilizes previous data. PSAs make use of these information to foresee client requirements and proactively fix problems before they proliferate.